Clinical Characteristics and Prognosis Analysis of Acinetobacter baumannii Bloodstream Infection Based on Propensity Matching
- PMID: 36474906
- PMCID: PMC9719707
- DOI: 10.2147/IDR.S387898
Clinical Characteristics and Prognosis Analysis of Acinetobacter baumannii Bloodstream Infection Based on Propensity Matching
Abstract
Purpose: In view of the fact that Acinetobacter baumannii bloodstream infection(BSI) is a great threat to human survival, early identification of the risk factors affecting prognosis will be of great benefit to the clinic.
Patients and methods: A propensity score matching method was used to collect patients identified with Acinetobacter baumannii BSI from 2016 to 2020 from a reputable hospital in China.
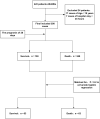
Results: A total of 398 patients were considered. According to the 28-day prognosis, they were divided into the survival group 150 (37.7%) and the death group 248 (62.3%), and the prognosis was analyzed. Subsequently, Propensity score matching was adjusted for variables with p-values <O.2 in the baseline data, equalized differences in baseline, multivariate paired logistics regression analysis was performed on 63 matched patients and showed that patients with Acinetobacter baumannii BSI who had higher SOFA scores at the time of infection, with septic shock, or mechanical ventilation were more likely to be fatally hit within 28 days and had a poor prognosis.
Conclusion: The existence of drug resistance with Acinetobacter baumannii only leads to Inappropriate empirical antibiotic therapy, ultimately, Inappropriate empirical antibiotic therapy was the direct predictor of mortality.
Keywords: Acinetobacter baumannii; bloodstream infection; inappropriate empirical antibiotic therapy; prognosis; propensity score matching.
© 2022 Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Construction and Validation of a Predictive Model for Mortality Risk in Patients with Acinetobacter baumannii Bloodstream Infection.Infect Drug Resist. 2024 Nov 26;17:5247-5260. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S491537. eCollection 2024. Infect Drug Resist. 2024. PMID: 39624638 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Factors That Affect Mortality Patients with Acinetobacter baumannii Bloodstream Infection.Infect Drug Resist. 2024 Sep 3;17:3825-3837. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S475073. eCollection 2024. Infect Drug Resist. 2024. PMID: 39247754 Free PMC article.
-
[Analysis of clinical manifestations and risk factors of mortality in Acinetobacter baumannii bloodstream infection].Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2016 Feb;55(2):121-6. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0578-1426.2016.02.011. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 26875581 Chinese.
-
[Analysis of risk factors on prognosis of Acinetobacter baumannii bloodstream infection].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2013 Aug;25(8):471-4. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2013.08.006. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2013. PMID: 24021042 Chinese.
-
Risk factors and predictors of carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii mortality in critically ill bacteraemic patients over a 6-year period (2010-15): antibiotics do matter.J Med Microbiol. 2017 Aug;66(8):1092-1101. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.000538. J Med Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28758623
Cited by
-
Acinetobacter baumannii: assessing susceptibility patterns, management practices, and mortality predictors in a tertiary teaching hospital in Lebanon.Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2023 Nov 29;12(1):136. doi: 10.1186/s13756-023-01343-8. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2023. PMID: 38031181 Free PMC article.
-
Construction and Validation of a Predictive Model for Mortality Risk in Patients with Acinetobacter baumannii Bloodstream Infection.Infect Drug Resist. 2024 Nov 26;17:5247-5260. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S491537. eCollection 2024. Infect Drug Resist. 2024. PMID: 39624638 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Factors That Affect Mortality Patients with Acinetobacter baumannii Bloodstream Infection.Infect Drug Resist. 2024 Sep 3;17:3825-3837. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S475073. eCollection 2024. Infect Drug Resist. 2024. PMID: 39247754 Free PMC article.
-
Excess mortality and long-term disability from healthcare-associated carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii infections: A nationwide population-based matched cohort study.PLoS One. 2023 Sep 11;18(9):e0291059. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0291059. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37695791 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro Activity of Eravacycline and Risk Factors for Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter Baumannii Infections in Patients with Respiratory Diseases: A Retrospective Cohort Study.Infect Drug Resist. 2025 Jun 25;18:3127-3136. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S519301. eCollection 2025. Infect Drug Resist. 2025. PMID: 40586076 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources