An Untargeted Metabolomics Workflow that Scales to Thousands of Samples for Population-Based Studies
- PMID: 36475608
- PMCID: PMC11018270
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.2c01270
An Untargeted Metabolomics Workflow that Scales to Thousands of Samples for Population-Based Studies
Abstract
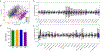
The success of precision medicine relies upon collecting data from many individuals at the population level. Although advancing technologies have made such large-scale studies increasingly feasible in some disciplines such as genomics, the standard workflows currently implemented in untargeted metabolomics were developed for small sample numbers and are limited by the processing of liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry data. Here we present an untargeted metabolomics workflow that is designed to support large-scale projects with thousands of biospecimens. Our strategy is to first evaluate a reference sample created by pooling aliquots of biospecimens from the cohort. The reference sample captures the chemical complexity of the biological matrix in a small number of analytical runs, which can subsequently be processed with conventional software such as XCMS. Although this generates thousands of so-called features, most do not correspond to unique compounds from the samples and can be filtered with established informatics tools. The features remaining represent a comprehensive set of biologically relevant reference chemicals that can then be extracted from the entire cohort's raw data on the basis of m/z values and retention times by using Skyline. To demonstrate applicability to large cohorts, we evaluated >2000 human plasma samples with our workflow. We focused our analysis on 360 identified compounds, but we also profiled >3000 unknowns from the plasma samples. As part of our workflow, we tested 14 different computational approaches for batch correction and found that a random forest-based approach outperformed the others. The corrected data revealed distinct profiles that were associated with the geographic location of participants.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interest Statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interests: The Patti laboratory has a research collaboration agreement with Thermo Fisher Scientific and receives financial support from Agilent Technologies. G.J.P is a scientific advisor for Cambridge Isotope Laboratories.
Figures
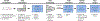

References
-
- FinnGen, a Global Research Project Focusing on Genome Data of 500,000 Finns, Launched. In EurekAlert! American Association for the Advancement of Science; EurekAlert! American Association for the Advancement of Science, 2017.
-
- Bycroft C; Freeman C; Petkova D; Band G; Elliott LT; Sharp K; Motyer A; Vukcevic D; Delaneau O; O’Connell J; Cortes A; Welsh S; Young A; Effingham M; McVean G; Leslie S; Allen N; Donnelly P; Marchini J The UK Biobank Resource with Deep Phenotyping and Genomic Data. Nature 2018, 562 (7726), 203–209. 10.1038/s41586-018-0579-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

