PmiR senses 2-methylisocitrate levels to regulate bacterial virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- PMID: 36475801
- PMCID: PMC9728974
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.add4220
PmiR senses 2-methylisocitrate levels to regulate bacterial virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
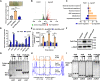
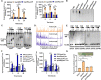
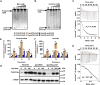
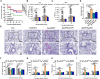
To adapt to changes in environmental cues, Pseudomonas aeruginosa produces an array of virulence factors to survive the host immune responses during infection. Metabolic products contribute to bacterial virulence; however, only a limited number of these signaling receptors have been explored in detail for their ability to modulate virulence in bacteria. Here, we characterize the metabolic pathway of 2-methylcitrate cycle in P. aeruginosa and unveil that PmiR served as a receptor of 2-methylisocitrate (MIC) to govern bacterial virulence. Crystallographic studies and structural-guided mutagenesis uncovered several residues crucial for PmiR's allosteric activation by MIC. We also demonstrated that PmiR directly repressed the pqs quorum-sensing system and subsequently inhibited pyocyanin production. Moreover, mutation of pmiR reduces bacterial survival in a mouse model of acute pneumonia infection. Collectively, this study identified P. aeruginosa PmiR as an important metabolic sensor for regulating expression of bacterial virulence genes to adapt to the harsh environments.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Coordinated regulation of anthranilate metabolism and bacterial virulence by the GntR family regulator MpaR in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Mol Microbiol. 2020 Nov;114(5):857-869. doi: 10.1111/mmi.14584. Epub 2020 Aug 18. Mol Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32748556
-
Pseudomonas quinolone signalling system: a component of quorum sensing cascade is a crucial player in the acute urinary tract infection caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Int J Med Microbiol. 2014 Nov;304(8):1199-208. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2014.08.013. Epub 2014 Sep 1. Int J Med Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25240873
-
Chlorogenic acid attenuates virulence factors and pathogenicity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by regulating quorum sensing.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019 Jan;103(2):903-915. doi: 10.1007/s00253-018-9482-7. Epub 2018 Nov 12. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 30421108
-
The third quorum-sensing system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Pseudomonas quinolone signal and the enigmatic PqsE protein.J Med Microbiol. 2020 Jan;69(1):25-34. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.001116. J Med Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 31794380 Review.
-
Quorum sensing by 2-alkyl-4-quinolones in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other bacterial species.Mol Biosyst. 2008 Sep;4(9):882-8. doi: 10.1039/b803796p. Epub 2008 Jun 30. Mol Biosyst. 2008. PMID: 18704225 Review.
Cited by
-
Bacteriophage protein Dap1 regulates evasion of antiphage immunity and Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence impacting phage therapy in mice.Nat Microbiol. 2024 Jul;9(7):1828-1841. doi: 10.1038/s41564-024-01719-5. Epub 2024 Jun 17. Nat Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38886583
-
E.PathDash, pathway activation analysis of publicly available pathogen gene expression data.mSystems. 2024 Nov 19;9(11):e0103024. doi: 10.1128/msystems.01030-24. Epub 2024 Oct 18. mSystems. 2024. PMID: 39422483 Free PMC article.
-
Fine particulate matter 2.5 induces susceptibility to Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection via expansion of PD-L1high neutrophils in mice.Respir Res. 2024 Feb 14;25(1):90. doi: 10.1186/s12931-023-02640-x. Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 38355515 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering allosterism of an Escherichia coli hexuronate metabolism regulator: UxuR.RSC Med Chem. 2025 Jun 30. doi: 10.1039/d5md00391a. Online ahead of print. RSC Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 40656839 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinase-aided amplification assay for rapid detection of imipenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa and rifampin-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Sep 10;14:1428827. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1428827. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39318475 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Horswill A. R., Dudding A. R., Escalante-Semerena J. C.,Studies of propionate toxicity in Salmonella enterica identify 2-methylcitrate as a potent inhibitor of cell growth. J. Biol. Chem. 276,19094–19101 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Dolan S. K., Wijaya A., Geddis S. M., Spring D. R., Silva-Rocha R., Welch M.,Loving the poison: The methylcitrate cycle and bacterial pathogenesis. Microbiology (Reading) 164,251–259 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Upton A. M., McKinney J. D.,Role of the methylcitrate cycle in propionate metabolism and detoxification in Mycobacterium smegmatis. Microbiology (Reading) 153,3973–3982 (2007). - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

