Ultra-processed food consumption and risk of colorectal cancer precursors: results from 3 prospective cohorts
- PMID: 36477589
- PMCID: PMC9905956
- DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djac221
Ultra-processed food consumption and risk of colorectal cancer precursors: results from 3 prospective cohorts
Abstract
Background: Growing evidence indicates the adverse effect of ultra-processed food (UPF) consumption. However, it remains unknown whether UPF consumption influences the risk of colorectal cancer (CRC) precursors, namely conventional adenomas and serrated lesions.
Methods: We drew data from the Nurses' Health Study, Nurses' Health Study II, and Health Professionals Follow-up Study, comprising 142 052 participants who had undergone at least 1 lower gastrointestinal endoscopy during follow-up. To handle multiple records per participants, we used multivariable logistic regression for clustered data to calculate odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) of colorectal polyps in relation to cumulative average consumption of UPFs. All statistical tests were 2-sided.
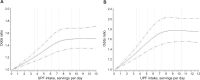
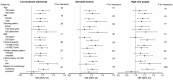
Results: We documented 11 644 patients with conventional adenomas and 10 478 with serrated lesions during 18-20 years of follow-up. Compared with participants in the lowest quintile of UPF consumption, those in the highest quintile had an increased risk of conventional adenomas (OR = 1.18, 95% CI = 1.11 to 1.26) and serrated lesions (OR = 1.20, 95% CI = 1.13 to 1.28). Similar results were found for high-risk polyps (ie, advanced adenomas and ≥10 mm serrated lesions; OR = 1.17, 95% CI = 1.07 to 1.28). These associations were slightly attenuated but remained statistically significant after further adjusting for body mass index, Western dietary pattern score, or individual dietary factors (fiber, folate, calcium, and vitamin D). The results remained essentially unchanged after excluding processed meat from total UPF intake.
Conclusions: Higher consumption of UPFs is associated with an increased risk of CRC precursors. UPFs might be a modifiable target for early prevention of CRC.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Comment in
-
Ultra-processed foods and colorectal neoplasia: is there a link?J Natl Cancer Inst. 2023 Feb 8;115(2):117-119. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djac222. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2023. PMID: 36478262 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209-249. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

