Patient stratification for determining optimal second-line and third-line therapy for type 2 diabetes: the TriMaster study
- PMID: 36477733
- PMCID: PMC7614216
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-022-02120-7
Patient stratification for determining optimal second-line and third-line therapy for type 2 diabetes: the TriMaster study
Abstract
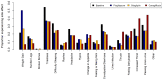
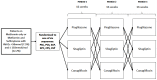
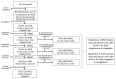
Precision medicine aims to treat an individual based on their clinical characteristics. A differential drug response, critical to using these features for therapy selection, has never been examined directly in type 2 diabetes. In this study, we tested two hypotheses: (1) individuals with body mass index (BMI) > 30 kg/m2, compared to BMI ≤ 30 kg/m2, have greater glucose lowering with thiazolidinediones than with DPP4 inhibitors, and (2) individuals with estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) 60-90 ml/min/1.73 m2, compared to eGFR >90 ml/min/1.73 m2, have greater glucose lowering with DPP4 inhibitors than with SGLT2 inhibitors. The primary endpoint for both hypotheses was the achieved HbA1c difference between strata for the two drugs. In total, 525 people with type 2 diabetes participated in this UK-based randomized, double-blind, three-way crossover trial of 16 weeks of treatment with each of sitagliptin 100 mg once daily, canagliflozin 100 mg once daily and pioglitazone 30 mg once daily added to metformin alone or metformin plus sulfonylurea. Overall, the achieved HbA1c was similar for the three drugs: pioglitazone 59.6 mmol/mol, sitagliptin 60.0 mmol/mol and canagliflozin 60.6 mmol/mol (P = 0.2). Participants with BMI > 30 kg/m2, compared to BMI ≤ 30 kg/m2, had a 2.88 mmol/mol (95% confidence interval (CI): 0.98, 4.79) lower HbA1c on pioglitazone than on sitagliptin (n = 356, P = 0.003). Participants with eGFR 60-90 ml/min/1.73 m2, compared to eGFR >90 ml/min/1.73 m2, had a 2.90 mmol/mol (95% CI: 1.19, 4.61) lower HbA1c on sitagliptin than on canagliflozin (n = 342, P = 0.001). There were 2,201 adverse events reported, and 447/525 (85%) randomized participants experienced an adverse event on at least one of the study drugs. In this precision medicine trial in type 2 diabetes, our findings support the use of simple, routinely available clinical measures to identify the drug class most likely to deliver the greatest glycemic reduction for a given patient. (ClinicalTrials.gov registration: NCT02653209 ; ISRCTN registration: 12039221 .).
© 2022. The Author(s) under exclusive license to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Comment in
-
Precision medicine approach improves HbA1c outcomes in T2DM.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2023 Mar;19(3):129. doi: 10.1038/s41574-022-00799-9. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2023. PMID: 36609555 No abstract available.
-
Trialing precision medicine for type 2 diabetes.Nat Med. 2023 Feb;29(2):309-310. doi: 10.1038/s41591-022-02168-5. Nat Med. 2023. PMID: 36737670 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

