Identification of immune cell function in breast cancer by integrating multiple single-cell data
- PMID: 36479102
- PMCID: PMC9719918
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1058239
Identification of immune cell function in breast cancer by integrating multiple single-cell data
Abstract
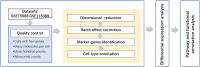
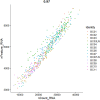
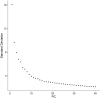
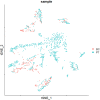
Breast cancer has now become the most commonly diagnosed cancer worldwide. It is a highly complex and heterogeneous disease that comprises distinct histological features and treatment response. With the development of molecular biology and immunology, immunotherapy has become a new field of breast cancer treatment. Identifying cell-type-specific genes critical to the immune microenvironment contributes to breast cancer treatment. Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) technology could serve as a powerful tool to analyze cellular genetic information at single-cell resolution and to uncover the gene expression status of each cell, thus allowing comprehensive assessment of intercellular heterogeneity. Because of the influence of sample size and sequencing depth, the specificity of genes in different cell types for breast cancer cannot be fully revealed. Therefore, the present study integrated two public breast cancer scRNA-seq datasets aiming to investigate the functions of different type of immune cells in tumor microenvironment. We identified total five significant differential expressed genes of B cells, T cells and macrophage and explored their functions and immune mechanisms in breast cancer. Finally, we performed functional annotation analyses using the top fifteen differentially expressed genes in each immune cell type to discover the immune-related pathways and gene ontology (GO) terms.
Keywords: T cell; functional analysis; immune cells; integration analysis; scRNA-seq.
Copyright © 2022 Zhang, Qin, Xu, Zhang and Zhao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Single-cell RNA sequencing in breast cancer: Understanding tumor heterogeneity and paving roads to individualized therapy.Cancer Commun (Lond). 2020 Aug;40(8):329-344. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12078. Epub 2020 Jul 12. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2020. PMID: 32654419 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integration of scRNA-Seq and Bulk RNA-Seq to Analyse the Heterogeneity of Ovarian Cancer Immune Cells and Establish a Molecular Risk Model.Front Oncol. 2021 Sep 21;11:711020. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.711020. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34621670 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of HBEGF+ fibroblasts in the remission of rheumatoid arthritis by integrating single-cell RNA sequencing datasets and bulk RNA sequencing datasets.Arthritis Res Ther. 2022 Sep 6;24(1):215. doi: 10.1186/s13075-022-02902-x. Arthritis Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 36068607 Free PMC article.
-
Leveraging single-cell transcriptomic data to uncover immune suppressive cancer cell subsets in triple-negative canine breast cancers.Front Vet Sci. 2024 Sep 23;11:1434617. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1434617. eCollection 2024. Front Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 39376916 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell RNA sequencing in cancer research.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Mar 1;40(1):81. doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-01874-1. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33648534 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploration of Key Immune-Related Transcriptomes Associated with Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity in Patients with Breast Cancer.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2023 Oct;23(9-10):329-348. doi: 10.1007/s12012-023-09806-5. Epub 2023 Sep 8. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 37684436 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell and machine learning approaches uncover intrinsic immune-evasion genes in the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma.Liver Res. 2024 Nov 12;8(4):282-294. doi: 10.1016/j.livres.2024.11.001. eCollection 2024 Dec. Liver Res. 2024. PMID: 39958919 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

