Continuous effectiveness and safety after a hospital-wide switch to adalimumab biosimilar: An observational study in rheumatoid arthritis patients
- PMID: 36479936
- PMCID: PMC9731312
- DOI: 10.1002/prp2.1025
Continuous effectiveness and safety after a hospital-wide switch to adalimumab biosimilar: An observational study in rheumatoid arthritis patients
Abstract
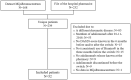
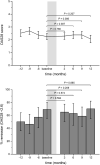
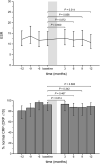
The objective of this study was to examine the maintenance of effect and safety after a hospital-wide switch for economic reasons from adalimumab originator Humira® to biosimilar Amgevita® in real-world rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients and patient satisfaction with the switch. We conducted a single-center retrospective observational study of RA patients on the course of their disease activity (DAS28, ESR, and CRP), health-related quality of life (SF-36), and functional disability (HAQ-DI) before and up to 1 year after the switch, supplemented with a cross-sectional survey on satisfaction and experienced side effects approximately 18 months after the switch. Treatment outcomes were analyzed with linear mixed modeling and generalized estimating equations. Of 52 RA patients sufficient data were available. Disease activity levels, the proportion of patients in remission, and SF-36 and HAQ-DI scores did not significantly change from before the switch. Overall, patients were satisfied with the switch. Three patients (7.9%) stopped the biosimilar due to side effects. In conclusion, switching to the adalimumab biosimilar did not result in increased disease activity or worse patient-reported outcomes. Also, there was no apparent evidence of increased side effects. Patients themselves were mostly satisfied with the switching experience.
Keywords: adalimumab; biological therapies; biosimilar; disease activity; rheumatoid arthritis; switch.
© 2022 The Authors. Pharmacology Research & Perspectives published by British Pharmacological Society and American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Klareskog L, van der Heijde D, de Jager JP, et al. Therapeutic effect of the combination of etanercept and methotrexate compared with each treatment alone in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: double‐blind randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2004;363(9410):675‐681. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(04)15640-7 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Breedveld FC, Weisman MH, Kavanaugh AF, et al. The PREMIER study: a multicenter, randomized, double‐blind clinical trial of combination therapy with adalimumab plus methotrexate versus methotrexate alone or adalimumab alone in patients with early, aggressive rheumatoid arthritis who had not had previous methotrexate treatment. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54(1):26‐37. doi:10.1002/art.21519 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

