IFITM proteins assist cellular uptake of diverse linked chemotypes
- PMID: 36480603
- PMCID: PMC9924227
- DOI: 10.1126/science.abl5829
IFITM proteins assist cellular uptake of diverse linked chemotypes
Abstract
The search for cell-permeable drugs has conventionally focused on low-molecular weight (MW), nonpolar, rigid chemical structures. However, emerging therapeutic strategies break traditional drug design rules by employing flexibly linked chemical entities composed of more than one ligand. Using complementary genome-scale chemical-genetic approaches we identified an endogenous chemical uptake pathway involving interferon-induced transmembrane proteins (IFITMs) that modulates the cell permeability of a prototypical biopic inhibitor of MTOR (RapaLink-1, MW: 1784 g/mol). We devised additional linked inhibitors targeting BCR-ABL1 (DasatiLink-1, MW: 1518 g/mol) and EIF4A1 (BisRoc-1, MW: 1466 g/mol), uptake of which was facilitated by IFITMs. We also found that IFITMs moderately assisted some proteolysis-targeting chimeras and examined the physicochemical requirements for involvement of this uptake pathway.
Figures
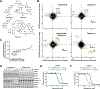
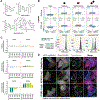

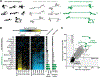
Comment in
-
Understanding cell permeability of bitopic molecules.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2023 Feb;22(2):99. doi: 10.1038/d41573-023-00009-9. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2023. PMID: 36631695 No abstract available.
References
-
- Lipinski CA, Lombardo F, Dominy BW, Feeney PJ, Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv Drug Deliver Rev. 23, 3–25 (1997). - PubMed
-
- Veber DF, Johnson SR, Cheng H-Y, Smith BR, Ward KW, Kopple KD, Molecular Properties That Influence the Oral Bioavailability of Drug Candidates. J Med Chem. 45, 2615–2623 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Ghose AK, Viswanadhan VN, Wendoloski JJ, A Knowledge-Based Approach in Designing Combinatorial or Medicinal Chemistry Libraries for Drug Discovery. 1. A Qualitative and Quantitative Characterization of Known Drug Databases. J Comb Chem. 1, 55–68 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Erez M, Takemori AE, Portoghese PS, Narcotic antagonistic potency of bivalent ligands which contain .beta.-naltrexamine. Evidence for simultaneous occupation of proximal recognition sites. J Med Chem. 25, 847–849 (1982). - PubMed
-
- Spencer D, Wandless T, Schreiber S, Crabtree G, Controlling signal transduction with synthetic ligands. Science. 262, 1019–1024 (1993). - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

