Lung ultrasound for evaluation of dyspnea: a pictorial review
- PMID: 36480902
- PMCID: PMC9732207
- DOI: 10.4266/acc.2022.00780
Lung ultrasound for evaluation of dyspnea: a pictorial review
Abstract
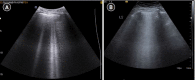
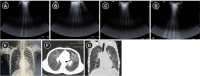
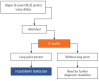
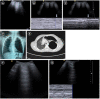
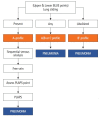
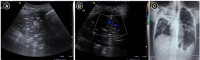
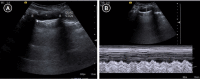
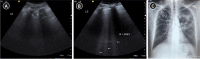
Lung ultrasound is based on the analysis of ultrasound artifacts generated by the pleura and air within the lungs. In recent years, lung ultrasound has emerged as an important alternative for quick evaluation of the patient at the bedside. Several techniques and protocols for performing lung ultrasound have been described in the literature, with the most popular one being the Bedside Lung Ultrasound in Emergency (BLUE) protocol which can be utilized to diagnose the cause of acute dyspnea at the bedside. We attempt to provide a simplified approach to understanding the physics behind the artifacts used in lung ultrasound, the imaging techniques, and the application of the BLUE protocol to diagnose the commonly presenting causes of acute dyspnea.
Keywords: artifacts; dyspnea; lung; pleura; ultrasound.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures




References
-
- Lichtenstein DA. BLUE protocol and FALLS-protocol: two applications of lung ultrasound in the critically ill. Chest. 2015;147:1659–70. - PubMed
-
- Feldman MK, Katyal S, Blackwood MS. US artifacts. Radiographics. 2009;29:1179–89. - PubMed
-
- Baad M, Lu ZF, Reiser I, Paushter D. Clinical significance of US artifacts. Radiographics. 2017;37:1408–23. - PubMed
-
- Jambrik Z, Monti S, Coppola V, Agricola E, Mottola G, Miniati M, et al. Usefulness of ultrasound lung comets as a nonradiologic sign of extravascular lung water. Am J Cardiol. 2004;93:1265–70. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources