Longitudinal Relationship Between Anemia and Statural Growth Impairment in Children and Adolescents With Nonglomerular CKD: Findings From the Chronic Kidney Disease in Children (CKiD) Study
- PMID: 36481700
- PMCID: PMC10038884
- DOI: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2022.09.019
Longitudinal Relationship Between Anemia and Statural Growth Impairment in Children and Adolescents With Nonglomerular CKD: Findings From the Chronic Kidney Disease in Children (CKiD) Study
Abstract
Rationale & objective: Anemia and statural growth impairment are both prevalent in children with nonglomerular chronic kidney disease (CKD) and are associated with poor quality of life and increased morbidity and mortality. However, to date no longitudinal studies have demonstrated a relationship between anemia and statural growth in this population.
Study design: The CKD in Children (CKiD) study is a multicenter prospective cohort study with over 15 years of follow-up observation.
Setting & participants: CKiD participants younger than 22 years with nonglomerular CKD who had not reached final adult height.
Exposure: Age-, sex-, and race-specific hemoglobin z score.
Outcome: Age- and sex-specific height z score.
Analytical approach: The relationship between hemoglobin and height was quantified using (1) multivariable repeated measures paired person-visit analysis, and (2) multivariable repeated measures linear mixed model analysis. Both models were adjusted for age, sex, body mass index, estimated glomerular filtration rate, acidosis, and medication use.
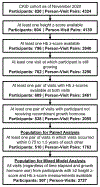
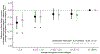
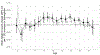
Results: Overall, 67% of the 510 participants studied had declining hemoglobin z score trajectories over the follow-up period, which included 1,763 person-visits. Compared with average hemoglobin z scores of≥0, average hemoglobin z scores of less than -1.0 were independently associated with significant growth impairment at the subsequent study visit, with height z score decline ranging from 0.24 to 0.35. Importantly, in 50% of cases hemoglobin z scores of less than -1.0 corresponded to hemoglobin values higher than those used as cutoffs defining anemia in the KDIGO clinical practice guideline for anemia in CKD. When stratified by age, the magnitude of the association peaked in participants aged 9 years. In line with paired-visit analyses, our mixed model analysis demonstrated that in participants with baseline hemoglobin z score less than -1.0, a hemoglobin z score decline over the follow-up period was associated with a statistically significant concurrent decrease in height z score.
Limitations: Limited ability to infer causality.
Conclusions: Hemoglobin decline is associated with growth impairment over time in children with mild to moderate nonglomerular CKD, even before hemoglobin levels reach the cutoffs that are currently used to define anemia in this population.
Keywords: Adolescent; anemia; children; chronic kidney disease (CKD); growth impairment; height z score; hemoglobin; pediatric CKD; short stature.
Copyright © 2022 National Kidney Foundation, Inc. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Adiposity, Sex, and Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Children With CKD: A Longitudinal Study of Youth Enrolled in the Chronic Kidney Disease in Children (CKiD) Study.Am J Kidney Dis. 2020 Aug;76(2):166-173. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2020.01.011. Epub 2020 May 7. Am J Kidney Dis. 2020. PMID: 32389356 Free PMC article.
-
Predictors of Rapid Progression of Glomerular and Nonglomerular Kidney Disease in Children and Adolescents: The Chronic Kidney Disease in Children (CKiD) Cohort.Am J Kidney Dis. 2015 Jun;65(6):878-88. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2015.01.008. Epub 2015 Mar 19. Am J Kidney Dis. 2015. PMID: 25799137 Free PMC article.
-
Associations Between Weight Loss, Kidney Function Decline, and Risk of ESRD in the Chronic Kidney Disease in Children (CKiD) Cohort Study.Am J Kidney Dis. 2018 May;71(5):648-656. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2017.08.013. Epub 2017 Nov 11. Am J Kidney Dis. 2018. PMID: 29132947 Free PMC article.
-
CKiD (CKD in children) prospective cohort study: a review of current findings.Am J Kidney Dis. 2012 Dec;60(6):1002-11. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2012.07.018. Epub 2012 Sep 28. Am J Kidney Dis. 2012. PMID: 23022429 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The CKiD study: overview and summary of findings related to kidney disease progression.Pediatr Nephrol. 2021 Mar;36(3):527-538. doi: 10.1007/s00467-019-04458-6. Epub 2020 Feb 3. Pediatr Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 32016626 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Response to oral iron therapy in children with anemia of chronic kidney disease.Pediatr Nephrol. 2024 Jan;39(1):233-242. doi: 10.1007/s00467-023-06048-z. Epub 2023 Jul 17. Pediatr Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 37458800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative efficacy of epoetin alfa vs. darbepoetin in children with chronic kidney disease: a systematic review, meta-analysis and cost-effectiveness analysis.J Nephrol. 2025 May 11. doi: 10.1007/s40620-025-02303-8. Online ahead of print. J Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40349276 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

