Anxiety onset in adolescents: a machine-learning prediction
- PMID: 36481929
- PMCID: PMC9908534
- DOI: 10.1038/s41380-022-01840-z
Anxiety onset in adolescents: a machine-learning prediction
Abstract
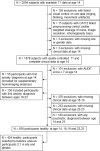
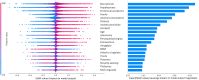
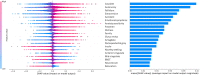
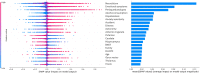
Recent longitudinal studies in youth have reported MRI correlates of prospective anxiety symptoms during adolescence, a vulnerable period for the onset of anxiety disorders. However, their predictive value has not been established. Individual prediction through machine-learning algorithms might help bridge the gap to clinical relevance. A voting classifier with Random Forest, Support Vector Machine and Logistic Regression algorithms was used to evaluate the predictive pertinence of gray matter volumes of interest and psychometric scores in the detection of prospective clinical anxiety. Participants with clinical anxiety at age 18-23 (N = 156) were investigated at age 14 along with healthy controls (N = 424). Shapley values were extracted for in-depth interpretation of feature importance. Prospective prediction of pooled anxiety disorders relied mostly on psychometric features and achieved moderate performance (area under the receiver operating curve = 0.68), while generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) prediction achieved similar performance. MRI regional volumes did not improve the prediction performance of prospective pooled anxiety disorders with respect to psychometric features alone, but they improved the prediction performance of GAD, with the caudate and pallidum volumes being among the most contributing features. To conclude, in non-anxious 14 year old adolescents, future clinical anxiety onset 4-8 years later could be individually predicted. Psychometric features such as neuroticism, hopelessness and emotional symptoms were the main contributors to pooled anxiety disorders prediction. Neuroanatomical data, such as caudate and pallidum volume, proved valuable for GAD and should be included in prospective clinical anxiety prediction in adolescents.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
TB served in an advisory or consultancy role for ADHS digital, Infectopharm, Lundbeck, Medice, Neurim Pharmaceuticals, Oberberg GmbH, Roche, and Takeda. He received conference support or speaker’s fee by Medice and Takeda. He has been involved in clinical trials conducted by Shire & Viforpharma. He received royalties from Hogrefe, Kohlhammer, CIP Medien, Oxford University Press. He has been involved in clinical trials conducted by Shire & Viforpharma. GB has received honoraria from General Electric Healthcare for teaching on scanner programming courses. LP served in an advisory or consultancy role for Roche and Viforpharm and received speaker’s fee by Shire. She received royalties from Hogrefe, Kohlhammer and Schattauer. The present work is unrelated to the above grants and relationships. The other authors report no biomedical commercial relationships or conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Merikangas KR, He JP, Burstein M, Swanson SA, Avenevoli S, Cui L, et al. Lifetime prevalence of mental disorders in US adolescents: results from the National Comorbidity Study-Adolescent Supplement (NCS-A) J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2010;49:980–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jaac.2010.05.017. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Moreno-Peral P, Conejo-Cerón S, Motrico E, Rodríguez-Morejón A, Fernández A, García-Campayo J, et al. Risk factors for the onset of panic and generalised anxiety disorders in the general adult population: a systematic review of cohort studies. J Affect Disord. 2014;168:337–48. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2014.06.021. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

