Association of wearable device-measured vigorous intermittent lifestyle physical activity with mortality
- PMID: 36482104
- PMCID: PMC9800274
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-022-02100-x
Association of wearable device-measured vigorous intermittent lifestyle physical activity with mortality
Abstract
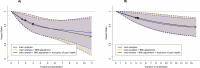
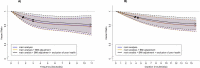
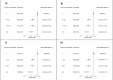
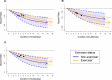
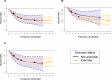
Wearable devices can capture unexplored movement patterns such as brief bursts of vigorous intermittent lifestyle physical activity (VILPA) that is embedded into everyday life, rather than being done as leisure time exercise. Here, we examined the association of VILPA with all-cause, cardiovascular disease (CVD) and cancer mortality in 25,241 nonexercisers (mean age 61.8 years, 14,178 women/11,063 men) in the UK Biobank. Over an average follow-up of 6.9 years, during which 852 deaths occurred, VILPA was inversely associated with all three of these outcomes in a near-linear fashion. Compared with participants who engaged in no VILPA, participants who engaged in VILPA at the sample median VILPA frequency of 3 length-standardized bouts per day (lasting 1 or 2 min each) showed a 38%-40% reduction in all-cause and cancer mortality risk and a 48%-49% reduction in CVD mortality risk. Moreover, the sample median VILPA duration of 4.4 min per day was associated with a 26%-30% reduction in all-cause and cancer mortality risk and a 32%-34% reduction in CVD mortality risk. We obtained similar results when repeating the above analyses for vigorous physical activity (VPA) in 62,344 UK Biobank participants who exercised (1,552 deaths, 35,290 women/27,054 men). These results indicate that small amounts of vigorous nonexercise physical activity are associated with substantially lower mortality. VILPA in nonexercisers appears to elicit similar effects to VPA in exercisers, suggesting that VILPA may be a suitable physical activity target, especially in people not able or willing to exercise.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors do not have any competing interests to declare.
Figures
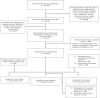
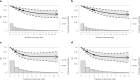
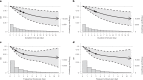

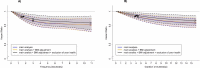
Comment in
-
Vigorous intermittent lifestyle physical activity improves mortality risk.Nat Med. 2022 Dec;28(12):2484-2485. doi: 10.1038/s41591-022-02101-w. Nat Med. 2022. PMID: 36513888 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

