Microglial diversity along the hippocampal longitudinal axis impacts synaptic plasticity in adult male mice under homeostatic conditions
- PMID: 36482444
- PMCID: PMC9730634
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-022-02655-z
Microglial diversity along the hippocampal longitudinal axis impacts synaptic plasticity in adult male mice under homeostatic conditions
Abstract
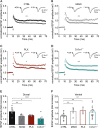
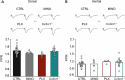
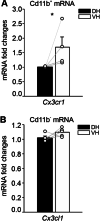
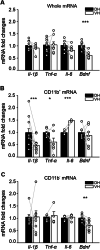
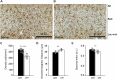
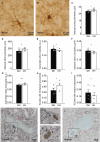
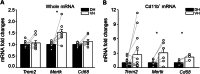
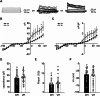
The hippocampus is a plastic brain area that shows functional segregation along its longitudinal axis, reflected by a higher level of long-term potentiation (LTP) in the CA1 region of the dorsal hippocampus (DH) compared to the ventral hippocampus (VH), but the mechanisms underlying this difference remain elusive. Numerous studies have highlighted the importance of microglia-neuronal communication in modulating synaptic transmission and hippocampal plasticity, although its role in physiological contexts is still largely unknown. We characterized in depth the features of microglia in the two hippocampal poles and investigated their contribution to CA1 plasticity under physiological conditions. We unveiled the influence of microglia in differentially modulating the amplitude of LTP in the DH and VH, showing that minocycline or PLX5622 treatment reduced LTP amplitude in the DH, while increasing it in the VH. This was recapitulated in Cx3cr1 knockout mice, indicating that microglia have a key role in setting the conditions for plasticity processes in a region-specific manner, and that the CX3CL1-CX3CR1 pathway is a key element in determining the basal level of CA1 LTP in the two regions. The observed LTP differences at the two poles were associated with transcriptional changes in the expression of genes encoding for Il-1, Tnf-α, Il-6, and Bdnf, essential players of neuronal plasticity. Furthermore, microglia in the CA1 SR region showed an increase in soma and a more extensive arborization, an increased prevalence of immature lysosomes accompanied by an elevation in mRNA expression of phagocytic markers Mertk and Cd68 and a surge in the expression of microglial outward K+ currents in the VH compared to DH, suggesting a distinct basal phenotypic state of microglia across the two hippocampal poles. Overall, we characterized the molecular, morphological, ultrastructural, and functional profile of microglia at the two poles, suggesting that modifications in hippocampal subregions related to different microglial statuses can contribute to dissect the phenotypical aspects of many diseases in which microglia are known to be involved.
Keywords: CX3CL1–CX3CR1 signaling; Cytokines; Dorsal hippocampus; K+ current; LTP; Microglial morphology; Microglial ultrastructure; Ventral hippocampus.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest or competing interests to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Nadel L. Dorsal and ventral hippocampal lesions and behavior. Physiol Behav. 1968;3(6):891–900. doi: 10.1016/0031-9384(68)90174-1. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- AR22117A67612A07/Avvio alla Ricerca 2021
- ERA-NET-NEURON/18/2018/National Research and Development Center, Poland to B.K
- PRIN 20178L7WRS_001/Ministero dell'Università e della Ricerca
- PRIN 2017HPTFFC_003/Ministero dell'Università e della Ricerca
- RF-2018-12366215/Ministero della salute, progetto di ricerca finalizzata
- AIRC2019 IG-23010/Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro
- 18/2018/ERA-NET-NEURON
- CONACYT/Mexican Council of Science and Technology Grant
- RGPIN-2014-05308/Natural Sciences and Research Council of Canada (NSERC) Discovery Grant
- FAR_DIP2021/FAR grant "Fondo di Ateneo per la Ricerca 2021"
- RM11916B7EE9E512/Fondo di Ateno per la Ricerca 2019
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

