Correlations of Myeloperoxidase (MPO), Adenosine deaminase (ADA), C-C motif chemokine 22 (CCL22), Tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNFα) and Interleukin-6 (IL-6) mRNA expression in the nasopharyngeal specimens with the diagnosis and severity of SARS-CoV-2 infections
- PMID: 36482706
- PMCID: PMC9809351
- DOI: 10.1080/22221751.2022.2157338
Correlations of Myeloperoxidase (MPO), Adenosine deaminase (ADA), C-C motif chemokine 22 (CCL22), Tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNFα) and Interleukin-6 (IL-6) mRNA expression in the nasopharyngeal specimens with the diagnosis and severity of SARS-CoV-2 infections
Abstract
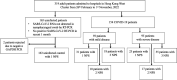
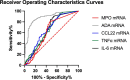
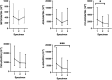
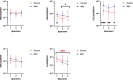
Cytokine dynamics in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) have been studied in blood but seldomly in respiratory specimens. We studied different cell markers and cytokines in fresh nasopharyngeal swab specimens for the diagnosis and for stratifying the severity of COVID-19. This was a retrospective case-control study comparing Myeloperoxidase (MPO), Adenosine deaminase (ADA), C-C motif chemokine ligand 22 (CCL22), Tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNFα) and Interleukin-6 (IL-6) mRNA expression in 490 (327 patients and 163 control) nasopharyngeal specimens from 317 (154 COVID-19 and 163 control) hospitalized patients. Of the 154 COVID-19 cases, 46 died. Both total and normalized MPO, ADA, CCL22, TNFα, and IL-6 mRNA expression levels were significantly higher in the nasopharyngeal specimens of infected patients when compared with controls, with ADA showing better performance (OR 5.703, 95% CI 3.424-9.500, p < 0.001). Receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curve showed that the cut-off value of normalized ADA mRNA level at 2.37 × 10-3 had a sensitivity of 81.8% and specificity of 83.4%. While patients with severe COVID-19 had more respiratory symptoms, and elevated lactate dehydrogenase, multivariate analysis showed that severe COVID-19 patients had lower CCL22 mRNA (OR 0.211, 95% CI 0.060-0.746, p = 0.016) in nasopharyngeal specimens, while lymphocyte count, C-reactive protein, and viral load in nasopharyngeal specimens did not correlate with disease severity. In summary, ADA appears to be a better biomarker to differentiate between infected and uninfected patients, while CCL22 has the potential in stratifying the severity of COVID-19.
Keywords: CCL22; COVID-19 severity; Nasopharyngeal specimen; adenosine deaminase; myeloperoxidase.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Epithelial Antimicrobial Peptide/Protein and Cytokine Expression Profiles Obtained from Nasopharyngeal Swabs of SARS-CoV-2-Infected and Non-Infected Subjects.Viruses. 2024 Sep 15;16(9):1471. doi: 10.3390/v16091471. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39339947 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of differential gene expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the nasopharyngeal milieu of mild & severe COVID-19 cases.PLoS One. 2022 Dec 30;17(12):e0279270. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0279270. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36584119 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of CCR5 signaling to treat COVID-19-associated cytokine storm: Case series of four critically ill patients treated with leronlimab.J Transl Autoimmun. 2021;4:100083. doi: 10.1016/j.jtauto.2021.100083. Epub 2021 Jan 6. J Transl Autoimmun. 2021. PMID: 33521616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum IL-23, IL-10, and TNF-α predict in-hospital mortality in COVID-19 patients.Front Immunol. 2023 May 22;14:1145840. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1145840. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37283736 Free PMC article.
-
Detection profile of SARS-CoV-2 using RT-PCR in different types of clinical specimens: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Med Virol. 2021 Feb;93(2):719-725. doi: 10.1002/jmv.26349. Epub 2020 Aug 2. J Med Virol. 2021. PMID: 32706393 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effects of Combined Treatment with Sodium Dichloroacetate and Sodium Valproate on the Genes in Inflammation- and Immune-Related Pathways in T Lymphocytes from Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection with Pneumonia: Sex-Related Differences.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Mar 16;16(3):409. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16030409. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38543303 Free PMC article.
-
The Causal Relationship between Plasma Myeloperoxidase Levels and Respiratory Tract Infections: A Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization Study.Mediators Inflamm. 2024 Mar 28;2024:6626706. doi: 10.1155/2024/6626706. eCollection 2024. Mediators Inflamm. 2024. PMID: 38576857 Free PMC article.
-
Adenosine Deaminase as a Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker for Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome.ACS Omega. 2024 Feb 23;9(9):11005-11011. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c00281. eCollection 2024 Mar 5. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 38463302 Free PMC article.
-
Patients Hospitalized with COVID-19 Demonstrate Distinct Plasma Cytokine and Chemokine Concentrations in vivo and TLR-Mediated Cytokine and Chemokine Production in Whole Blood in vitro.J Innate Immun. 2025;17(1):288-301. doi: 10.1159/000545432. Epub 2025 May 28. J Innate Immun. 2025. PMID: 40435967 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in Adenosine Deaminase Activity and Endothelial Dysfunction after Mild Coronavirus Disease-2019.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 24;24(17):13140. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713140. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37685949 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO . WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) dashboard. Available from: https://covid19.who.int/.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
