Protein overexpression can induce the elongation of cell membrane nanodomains
- PMID: 36482718
- PMCID: PMC10257090
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2022.12.009
Protein overexpression can induce the elongation of cell membrane nanodomains
Abstract
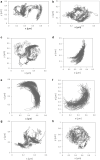
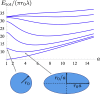
In cell membranes, proteins and lipids are organized into submicrometric nanodomains of varying sizes, shapes, and compositions, performing specific functions. Despite their biological importance, the detailed morphology of these nanodomains remains unknown. Not only can they hardly be observed by conventional microscopy due to their small size, but there is no full consensus on the theoretical models to describe their structuring and their shapes. Here, we use a combination of analytical calculations and Monte Carlo simulations based upon a model coupling membrane composition and shape to show that increasing protein concentration leads to an elongation of membrane nanodomains. The results are corroborated by single-particle tracking measurements on HIV receptors, whose level of expression in the membrane of specifically designed living cells can be tuned. These findings highlight that protein abundance can modulate nanodomain shape and potentially their biological function. Beyond biomembranes, this mesopatterning mechanism is of relevance in several soft-matter systems because it relies on generic physical arguments.
Copyright © 2022 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Singer S.J., Nicolson G.L. The fluid mosaic model of the structure of cell membranes. Science. 1972;175:720–731. - PubMed
-
- Jacobson K., Sheets E., Simson R. Revisiting the fluid mosaic model of membranes. Science. 1995;268:1441–1442. - PubMed
-
- Kusumi A., Fujiwara T.K., et al. Suzuki K.G.N. Dynamic organizing principles of the plasma membrane that regulate signal transduction: commemorating the fortieth anniversary of Singer and Nicolson’s fluid-mosaic model. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2012;28:215–250. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

