Establishment of Reference Values for Early Auditory Preverbal Skills of Children with Cochlear Implants
- PMID: 36482731
- PMCID: PMC9742715
- DOI: 10.1177/23312165221128435
Establishment of Reference Values for Early Auditory Preverbal Skills of Children with Cochlear Implants
Abstract
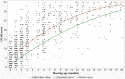
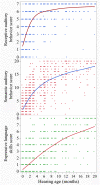
Auditory and verbal abilities of children with early cochlear implant (CI) surgery usually take some time to develop, and a reference index of early development for horizontal comparisons is urgently needed to guide the mapping process and adjust rehabilitation programs. Therefore, the aim of this study was to establish a reference value for early auditory preverbal skills development in children with CI and investigate the developmental curve and influencing factors for these children. The LittlEARS® Auditory Questionnaire (LEAQ) scores of 287 eligible Chinese participants were obtained at 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, 12, 18, 24, 28, and 36 months interval after CI activation. The median and standard deviation of the LEAQ score of each hearing stage for these children with different activation ages were calculated to establish the reference values. Quadratic regression was conducted to fit the expected developmental curve of the LEAQ score ( [0 to 20 months]). With a linear mixed-effects model, we found that the receptive auditory behavior increased rapidly after CI activation, while expressive language skills developed at a steady rate. We also found that the following factors all significantly influenced the LEAQ: the duration of CI use, the development quotient, age of implantation and activation, and the presence of large vestibular aqueduct syndrome or auditory neuropathy spectrum disorder. The reference values and the expected developmental curve for the LEAQ in children with CI established by the present study provides guidance to clinicians and parents as well as realistic expectations regarding language and speech outcomes.
Keywords: auditory development; children; cochlear implant; littlEARS® auditory questionnaire; mandarin.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Early auditory preverbal skills development in Mandarin speaking children with cochlear implants.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2015 Jan;79(1):71-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2014.11.010. Epub 2014 Nov 15. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2015. PMID: 25434480
-
Early auditory skills development in Mandarin speaking children after bilateral cochlear implantation.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2018 Nov;114:153-158. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2018.08.039. Epub 2018 Sep 1. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2018. PMID: 30262356
-
Validation of the LittlEARS Auditory Questionnaire in cochlear implanted infants and toddlers.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2017 Feb;93:107-116. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2016.12.024. Epub 2016 Dec 26. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2017. PMID: 28109480
-
[Cochlear implant in children: rational, indications and cost/efficacy].Minerva Pediatr. 2013 Jun;65(3):325-39. Minerva Pediatr. 2013. PMID: 23685383 Review. Italian.
-
Cochlear implantation in children with anomalous cochleovestibular anatomy.Laryngoscope. 2005 Jan;115(1 Pt 2 Suppl 106):1-26. doi: 10.1097/00005537-200501001-00001. Laryngoscope. 2005. PMID: 15626926 Review.
References
-
- Attias J., Greenstein T., Peled M., Ulanovski D., Wohlgelernter J., Raveh E. (2017). Auditory performance and electrical stimulation measures in cochlear implant recipients with auditory neuropathy compared with severe to profound sensorineural hearing loss. Ear and Hearing, 38(2), 184–193. 10.1097/AUD.0000000000000384 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Coez A., Fillon L., Saitovitch A., Rutten C., Marlin S., Boisgontier J., Boddaert N. (2021). Arterial spin labeling brain MRI study to evaluate the impact of deafness on cerebral perfusion in 79 children before cochlear implantation. Neuroimage. Clinical, 29(2021), 102510. 10.1016/j.nicl.2020.102510 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Coninx F., Weichbold V., Tsiakpini L., Autrique E., Bescond G., Tamas L., Brachmaier J. (2009). Validation of the LittlEARS((R)) Auditory Questionnaire in children with normal hearing. International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology, 73(12), 1761–1768. 10.1016/j.ijporl.2009.09.036 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

