The effects of an 8-week hypopressive exercise training program on urinary incontinence and pelvic floor muscle activation: A randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 36482844
- PMCID: PMC10107869
- DOI: 10.1002/nau.25110
The effects of an 8-week hypopressive exercise training program on urinary incontinence and pelvic floor muscle activation: A randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Pelvic floor dysfunction and urinary incontinence are two of the most frequent gynecological problems, and pelvic floor muscle training is recommended as a first-line treatment, with new approaches such as hypopressive exercises. This study aimed to analyze the efficacy of an 8-week supervised training program of hypopressive exercises on pelvic floor muscle strength and urinary incontinence symptomatology.
Design: Blinded randomized controlled trial.
Settings: Women with pelvic floor dysfunction and urinary incontinence symptoms, aged 18-60 years.
Participants: A total of 117 participants were randomly allocated to the hypopressive exercises group (n = 62) or a control group that received no intervention (n = 55) and completed the study.
Main outcome measures: Clinical and sociodemographic data were collected, as well as pelvic floor muscle strength (using the Modified Oxford Scale); the genital prolapse symptoms, colorectal symptoms, and urinary symptoms (with the Pelvic Floor Distress Inventory [PFDI-20]); the impact of pelvic floor disorders (PFD) on women's lives (with the Pelvic Floor Impact Questionnaire [PFIQ-7]); and the severity of urinary incontinence symptoms (using the International Consultation on Incontinence Questionnaire [ICIQ]).
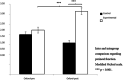
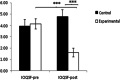
Results: The results showed an improvement in the hypopressive group in the pelvic floor muscle strength F (1117) = 89.514, p < 0.001, a significantly lower score for the PFIQ7 total score, t (112) = 28.895, p < 0.001 and FPDI20 t (112) = 7.037, p < 0.001 as well as an improvement in ICIQ-SF values after 8 weeks of intervention in comparison with the control group.
Conclusions: After performing an 8-week of hipopressive exercises intervention, a decrease in pelvic floor disorders associated symptoms can be observed. In addition, pelvic floor muscle contractility is improved and a decrease in severity and symptoms associated with urinary incontinence has been reported.
Keywords: hypopressive exercise; pelvic floor muscle; pelvic floor muscle training; pelvic organ prolapse; urinary incontinence.
© 2022 The Authors. Neurourology and Urodynamics published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effects of hypopressive exercise associated with aerobic and muscle strength training on the treatment of fatigue, urinary incontinence symptoms, sexual function, and quality of life in women treated for gynecologic cancer: A randomized clinical trial protocol.Medwave. 2024 Aug 13;24(7):e2906. doi: 10.5867/medwave.2024.07.2906. Medwave. 2024. PMID: 39137366
-
Effect of an abdominal hypopressive technique programme on pelvic floor muscle tone and urinary incontinence in women: a randomised crossover trial.Physiotherapy. 2020 Sep;108:37-44. doi: 10.1016/j.physio.2020.02.004. Epub 2020 Feb 19. Physiotherapy. 2020. PMID: 32707289 Clinical Trial.
-
Does pelvic floor muscle training abolish symptoms of urinary incontinence? A randomized controlled trial.Clin Rehabil. 2015 Jun;29(6):525-37. doi: 10.1177/0269215514546768. Epub 2014 Aug 20. Clin Rehabil. 2015. PMID: 25142280 Clinical Trial.
-
Pelvic Floor Dysfunction And Its Effect On Quality Of Sexual Life.Sex Med Rev. 2019 Oct;7(4):559-564. doi: 10.1016/j.sxmr.2019.05.007. Epub 2019 Jul 24. Sex Med Rev. 2019. PMID: 31351916 Review.
-
Effects of bariatric surgery on pelvic floor disorders in obese women: a meta-analysis.Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2017 Aug;296(2):181-189. doi: 10.1007/s00404-017-4415-8. Epub 2017 Jun 22. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2017. PMID: 28643025 Review.
Cited by
-
Application effect of pelvic floor function exercise based on health belief model in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia after electrocautery.Int Urol Nephrol. 2025 Apr 25. doi: 10.1007/s11255-025-04454-w. Online ahead of print. Int Urol Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40279078
-
Effectiveness of radiofrequency and exercise-based rehabilitation on symptoms associated with pelvic floor dysfunction in breast cancer patients: A study protocol.PLoS One. 2025 Aug 29;20(8):e0330156. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0330156. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40880350 Free PMC article.
-
The Efficacy of Pelvic Floor Rehabilitation in the Treatment of Urinary Incontinence in Female Athletes: A Systematic Review.Sports (Basel). 2024 Dec 5;12(12):338. doi: 10.3390/sports12120338. Sports (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39728878 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Hypopressive Abdominal Training on Ventilatory Capacity and Quality of Life: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Healthcare (Basel). 2024 Apr 25;12(9):893. doi: 10.3390/healthcare12090893. Healthcare (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38727450 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of Urinary Incontinence in Female Professional Soccer Players by Category and Specific Position: A Comparative Study with a Control Group.Healthcare (Basel). 2024 Dec 7;12(23):2478. doi: 10.3390/healthcare12232478. Healthcare (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39685100 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

