Transcriptomic meta-analysis reveals unannotated long non-coding RNAs related to the immune response in sheep
- PMID: 36482891
- PMCID: PMC9725098
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1067350
Transcriptomic meta-analysis reveals unannotated long non-coding RNAs related to the immune response in sheep
Abstract
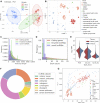
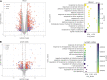
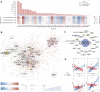
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are involved in several biological processes, including the immune system response to pathogens and vaccines. The annotation and functional characterization of lncRNAs is more advanced in humans than in livestock species. Here, we take advantage of the increasing number of high-throughput functional experiments deposited in public databases in order to uniformly analyse, profile unannotated lncRNAs and integrate 422 ovine RNA-seq samples from the ovine immune system. We identified 12302 unannotated lncRNA genes with support from independent CAGE-seq and histone modification ChIP-seq assays. Unannotated lncRNAs showed low expression levels and sequence conservation across other mammal species. There were differences in expression levels depending on the genomic location-based lncRNA classification. Differential expression analyses between unstimulated and samples stimulated with pathogen infection or vaccination resulted in hundreds of lncRNAs with changed expression. Gene co-expression analyses revealed immune gene-enriched clusters associated with immune system activation and related to interferon signalling, antiviral response or endoplasmic reticulum stress. Besides, differential co-expression networks were constructed in order to find condition-specific relationships between coding genes and lncRNAs. Overall, using a diverse set of immune system samples and bioinformatic approaches we identify several ovine lncRNAs associated with the response to an external stimulus. These findings help in the improvement of the ovine lncRNA catalogue and provide sheep-specific evidence for the implication in the general immune response for several lncRNAs.
Keywords: RNA-seq; genomics; immune system; lncRNAs; sheep; transcriptomics.
Copyright © 2022 Bilbao-Arribas and Jugo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

