Metabolic reprogramming by miRNAs in the tumor microenvironment: Focused on immunometabolism
- PMID: 36483029
- PMCID: PMC9723351
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1042196
Metabolic reprogramming by miRNAs in the tumor microenvironment: Focused on immunometabolism
Abstract
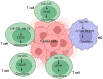
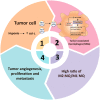
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are emerging as a significant modulator of immunity, and their abnormal expression/activity has been linked to numerous human disorders, such as cancer. It is now known that miRNAs potentially modulate the production of several metabolic processes in tumor-associated immune cells and indirectly via different metabolic enzymes that affect tumor-associated signaling cascades. For instance, Let-7 has been identified as a crucial modulator for the long-lasting survival of CD8+ T cells (naive phenotypes) in cancer by altering their metabolism. Furthermore, in T cells, it has been found that enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2) expression is controlled via glycolytic metabolism through miRNAs in patients with ovarian cancer. On the other hand, immunometabolism has shown us that cellular metabolic reactions and processes not only generate ATP and biosynthetic intermediates but also modulate the immune system and inflammatory processes. Based on recent studies, new and encouraging approaches to cancer involving the modification of miRNAs in immune cell metabolism are currently being investigated, providing insight into promising targets for therapeutic strategies based on the pivotal role of immunometabolism in cancer. Throughout this overview, we explore and describe the significance of miRNAs in cancer and immune cell metabolism.
Keywords: MicroRNAs; cancer; immune cell; immunometabolism; metabolism.
Copyright © 2022 Alshahrani, Ibrahim, Jalil, Altoum, Achmad, Zabibah, Gabr, Ramírez-Coronel, Alameri, Qasim, Karampoor and Mirzaei.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-mediated metabolic regulation of immune cells in cancer: an updated review.Front Immunol. 2024 Jun 28;15:1424909. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1424909. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39007129 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting immunometabolism against acute lung injury.Clin Immunol. 2023 Apr;249:109289. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2023.109289. Epub 2023 Mar 12. Clin Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36918041 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Complex cross-talk between EZH2 and miRNAs confers hallmark characteristics and shapes the tumor microenvironment.Epigenomics. 2022 Jun;14(11):699-709. doi: 10.2217/epi-2021-0534. Epub 2022 May 16. Epigenomics. 2022. PMID: 35574589 Review.
-
Discovering the strength of immunometabolism in cancer therapy: Employing metabolic pathways to enhance immune responses.Cell Biochem Funct. 2024 Mar;42(2):e3934. doi: 10.1002/cbf.3934. Cell Biochem Funct. 2024. PMID: 38379261 Review.
-
Therapeutic Metabolic Reprograming Using microRNAs: From Cancer to HIV Infection.Genes (Basel). 2022 Jan 29;13(2):273. doi: 10.3390/genes13020273. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35205318 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Reactive oxygen species induced by SARS-CoV-2 infection can induce EMT in solid tumors: Potential role of COVID-19 in chemo-resistance and metastasis.Heliyon. 2024 Nov 8;10(22):e40297. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e40297. eCollection 2024 Nov 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39624316 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs in Cancer Immunology: Master Regulators of the Tumor Microenvironment and Immune Evasion, with Therapeutic Potential.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jun 27;17(13):2172. doi: 10.3390/cancers17132172. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40647470 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deciphering Medulloblastoma: Epigenetic and Metabolic Changes Driving Tumorigenesis and Treatment Outcomes.Biomedicines. 2025 Aug 4;13(8):1898. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13081898. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40868156 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of mitochondrial/metabolic axis in development of tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer.Hum Cell. 2023 Nov;36(6):1877-1886. doi: 10.1007/s13577-023-00977-5. Epub 2023 Aug 30. Hum Cell. 2023. PMID: 37646973 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-mediated metabolic regulation of immune cells in cancer: an updated review.Front Immunol. 2024 Jun 28;15:1424909. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1424909. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39007129 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

