Pelvic Insufficiency Fractures and Bone Pain after Radiation Therapy for Anal Cancer: Relation to Pelvic Bone Dose-Volume Parameters
- PMID: 36483064
- PMCID: PMC9723308
- DOI: 10.1016/j.adro.2022.101110
Pelvic Insufficiency Fractures and Bone Pain after Radiation Therapy for Anal Cancer: Relation to Pelvic Bone Dose-Volume Parameters
Abstract
Purpose: Chemoradiation therapy is the primary treatment for anal cancer. Radiation therapy (RT) can weaken the pelvic bone structure, but the risk of pelvic insufficiency fractures (PIFs) and derived pain in anal cancer is not yet established. We determined the frequency of symptomatic PIFs after RT for anal cancer and related this to radiation dose to specific pelvic bone substructures.
Methods and materials: In a prospective setting, patients treated with RT for anal cancer had magnetic resonance imaging 1 year after RT. PIFs were mapped to 17 different bone sites, and we constructed a guideline for detailed delineation of pelvic bone substructures. Patients were interviewed regarding pain and scored according to Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Effects. Dose-volume relationships for specific pelvic bone substructures and PIFs were determined for V20 to V40 Gy mean and maximum doses.
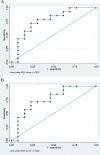
Results: Twenty-seven patients were included, and 51.9% had PIFs primarily located in the alae of the sacral bone. Patients with PIFs had significantly more pelvic pain (86% vs 23%, P = .001) and 43% had grade 2 bone pain. Dose-volume parameters for sacral bone and sacral alae were significantly higher in patients with PIFs (P < .05). V30 Gy (%) for sacral bone and alae implied an area under the curve of 0.764 and 0.758, respectively, in receiver operating characteristic analyses.
Conclusions: We observed a high risk of PIFs in patients treated with RT for anal cancer 1 year after treatment. A significant proportion had pain in the sites where PIFs were most frequently found. Radiation dose to pelvic bone substructures revealed relation to risk of PIFs and can be used for plan optimization in future clinical trials.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pelvic insufficiency fractures, dose volume parameters and plan optimization after radiotherapy for rectal cancer.Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 2019 Sep 10;19:72-76. doi: 10.1016/j.ctro.2019.09.001. eCollection 2019 Nov. Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31646202 Free PMC article.
-
Pelvic insufficiency fractures after intensity modulated radiation therapy combined with chemotherapy for cervix carcinoma: Incidence and impact of bone mineral density.Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 2023 Jun 12;41:100650. doi: 10.1016/j.ctro.2023.100650. eCollection 2023 Jul. Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37441540 Free PMC article.
-
Pelvic insufficiency fractures and pelvic bone metastases after neoadjuvant (chemo)radiotherapy for rectal cancer.Acta Oncol. 2023 Oct;62(10):1295-1300. doi: 10.1080/0284186X.2023.2252168. Epub 2023 Sep 1. Acta Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37656773
-
Radiation-Induced Insufficiency Fractures After Pelvic Irradiation for Gynecologic Malignancies: A Systematic Review.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2020 Nov 1;108(3):620-634. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2020.05.013. Epub 2020 May 19. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2020. PMID: 32442476
-
Pelvic Insufficiency Fractures After External Beam Radiation Therapy for Gynecologic Cancers: A Meta-analysis and Meta-regression of 3929 Patients.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2020 Mar 1;106(3):475-484. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2019.09.012. Epub 2019 Sep 30. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2020. PMID: 31580930
Cited by
-
Radiation-Related Fractures after Radical Radiotherapy for Cervical and Endometrial Cancers: Are There Any Differences?Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Apr 12;14(8):810. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14080810. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38667456 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Pelvic External Beam Radiation Therapy on Bone Mineral Density: A Secondary Analysis of a Phase 3 Randomized Controlled Trial.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2024 May 1;119(1):119-126. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2023.10.046. Epub 2023 Nov 3. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2024. PMID: 37924987 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Patient-reported outcomes after chemoradiotherapy for anal cancer.Acta Oncol. 2025 Jul 30;64:1005-1013. doi: 10.2340/1651-226X.2025.43636. Acta Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40734575 Free PMC article.
-
Radio(chemo)therapy with curative intent for anal cancer - effectiveness and toxicity in elderly vs. younger patients.Front Oncol. 2025 May 16;15:1567655. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1567655. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40452840 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Higham CE, health Faithfull S.Bone, radiotherapy pelvic. Clin Oncol. 2015;27:668–678. - PubMed
-
- Oh D, Huh SJ, Nam H, et al. Pelvic insufficiency fracture after pelvic radiotherapy for cervical cancer: Analysis of risk factors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008;70:1183–1188. - PubMed
-
- Tomaszewski JM, Link E, Leong T, et al. Twenty-five-year experience with radical chemoradiation for anal cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012;83:552–558. - PubMed
-
- Baxter NN, Habermann EB, Tepper JE, Durham SB, Virnig BA. Risk of pelvic fractures in older women following pelvic irradiation. JAMA. 2005;294:2587–2593. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

