The combination effect of meropenem/sulbactam/polymyxin-B on the pharmacodynamic parameters for mutant selection windows against carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii
- PMID: 36483204
- PMCID: PMC9723340
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1024702
The combination effect of meropenem/sulbactam/polymyxin-B on the pharmacodynamic parameters for mutant selection windows against carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii
Abstract
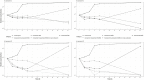
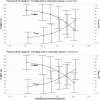
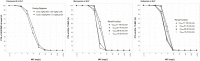
The objective of this study was to evaluate whether combinations of sulbactam, meropenem, and polymyxin-B could reduce or close the gap of mutant selection window (MSW) of individual antibiotics against Acinetobacter baumannii harboring OXA-23. MICs of three antimicrobials used alone and in combination (meropenem/polymyxin-B or meropenem/polymyxin-B/sulbactam) were obtained in 11 clinical isolates and mutant prevention concentrations were determined in 4 of the 11 isolates. All isolates were resistant to meropenem or polymyxin-B. Combining meropenem and polymyxin-B with or without sulbactam resulted in synergistic bactericidal activities. Pharmacokinetic (PK) simulations of drug concentrations in the blood and epithelial lining fluid coupled with pharmacodynamic (PD) evaluations revealed that the fractions of time over the 24-h in terms of free drug concentration within the MSW (fTMSW) and above the MPC (fT>MPC) were optimized by combination therapy. The resultant clinical regimens of meropenem, polymyxin-B, and sulbactam evaluated in the PK-PD analysis were 2 g q8h, 2.5 mg/kg loading dose followed by 1.5 mg/kg q12h, and 3 g q8h, respectively, in patients with normal renal function. Subsequent corresponding equivalent exposure regimens would depend on the extent of renal failure. The overall results indicate that combination antibiotics consisting of sulbactam/meropenem/polymyxin-B can confer potential efficacy against A. baumannii harboring OXA-23, and reduce the opportunity for bacteria to develop further resistance. This study provides a framework for pharmacodynamic evaluation of drug-resistant mutant suppression in an antimicrobial co-administration setting. The results thereby lay the groundwork for additional studies and future clinical confirmation is warranted.
Keywords: Acinetobacter baumannii; OXA-23; meropenem; pharmacodynamics; polymyxin-B; sulbactam.
Copyright © 2022 Zhang, Diao, Liu, Wang, Liu, Zhu, Feng, Tang, Oo, Zhu, Lv, Yu, Sy and Zhu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of amikacin, polymyxin-B, and sulbactam combination on the pharmacodynamic indices of mutant selection against multi-drug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii.Front Microbiol. 2022 Oct 20;13:1013939. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1013939. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36338049 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacodynamic Effects of Sulbactam/Meropenem/Polymyxin-B Combination Against Extremely Drug Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Using Checkerboard Information.Microb Drug Resist. 2019 Nov;25(9):1266-1274. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2018.0283. Epub 2019 Jun 19. Microb Drug Resist. 2019. PMID: 31216222
-
Minocycline Alone and in Combination with Polymyxin B, Meropenem, and Sulbactam against Carbapenem-Susceptible and -Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in an In Vitro Pharmacodynamic Model.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2021 Feb 17;65(3):e01680-20. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01680-20. Print 2021 Feb 17. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2021. PMID: 33318006 Free PMC article.
-
Non-polymyxin-based combinations as potential alternatives in treatment against carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii infections.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020 Oct;56(4):106115. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106115. Epub 2020 Jul 25. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020. PMID: 32721600
-
An Appraisal of the Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Properties of Meropenem-Vaborbactam.Infect Dis Ther. 2020 Dec;9(4):769-784. doi: 10.1007/s40121-020-00344-z. Epub 2020 Oct 6. Infect Dis Ther. 2020. PMID: 33025557 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Testing the mutant selection window hypothesis with meropenem: In vitro model study with OXA-48-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae.PLoS One. 2023 Aug 4;18(8):e0288660. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0288660. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37540701 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomics revealed mechanism for the synergistic effect of sulbactam, polymyxin-B and amikacin combination against Acinetobacter baumannii.Front Microbiol. 2023 Jun 29;14:1217270. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1217270. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37455727 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Evaluation of Aztreonam/Amoxicillin/Clavulanate Combination against New Delhi Metallo-β-Lactamase and Serine-β-Lactamase Co-Producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jan 11;15(1):251. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15010251. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36678879 Free PMC article.
-
Geographical mapping and temporal trends of Acinetobacter baumannii carbapenem resistance: A comprehensive meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2024 Dec 16;19(12):e0311124. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0311124. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39680587 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al Atrouni A., Hamze M., Jisr T., Lemarie C., Eveillard M., Joly-Guillou M. L., et al. . (2016). Wide spread of OXA-23-producing carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii belonging to clonal complex II in different hospitals in Lebanon. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 52, 29–36. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2016.09.017, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

