Trends in hospital antibiotic utilization during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic: A multicenter interrupted time-series analysis
- PMID: 36483375
- PMCID: PMC9726493
- DOI: 10.1017/ash.2022.268
Trends in hospital antibiotic utilization during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic: A multicenter interrupted time-series analysis
Abstract
Objective: To describe the evolution of respiratory antibiotic prescribing during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic across 3 large hospitals that maintained antimicrobial stewardship services throughout the pandemic.
Design: Retrospective interrupted time-series analysis.
Setting: A multicenter study was conducted including medical and intensive care units (ICUs) from 3 hospitals within a Canadian epicenter for COVID-19.
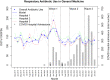
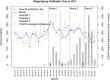
Methods: Interrupted time-series analysis was used to analyze rates of respiratory antibiotic utilization measured in days of therapy per 1,000 patient days (DOT/1,000 PD) in medical units and ICUs. Each of the first 3 waves of the pandemic were compared to the baseline.
Results: Within the medical units, use of respiratory antibiotics increased during the first wave of the pandemic (rate ratio [RR], 1.76; 95% CI, 1.38-2.25) but returned to the baseline in waves 2 and 3 despite more COVID-19 admissions. In ICU, the use of respiratory antibiotics increased in wave 1 (RR, 1.30; 95% CI, 1.16-1.46) and wave 2 of the pandemic (RR, 1.21; 95% CI, 1.11-1.33) and returned to the baseline in the third wave, which had the most COVID-19 admissions.
Conclusions: After an initial surge in respiratory antibiotic prescribing, we observed the normalization of prescribing trends at 3 large hospitals throughout the COVID-19 pandemic. This trend may have been due to the timely generation of new research and guidelines developed with frontline clinicians, allowing for the active application of new research to clinical practice.
© The Author(s) 2022.
Figures
References
-
- City of Toronto COVID-19: case counts. City of Toronto website. https://www.toronto.ca/home/covid-19/covid-19-latest-city-of-toronto-new.... Accessed February 22, 2022.
-
- Accreditation Canada. Required Organizational Practices: 2020. Handbook. Ottawa, Canada: Accreditation Canada; 2020.
-
- Peragine C, Walker SAN, Simor A, Walker SE, Kiss A, Leis JA. Impact of a comprehensive antimicrobial stewardship program on institutional burden of antimicrobial resistance: a 14-year controlled interrupted time-series study. Clin Infect Dis 2020;71:2897–2904. - PubMed
-
- Dellit TH, Owens RC, McGowan JE, et al. Infectious Diseases Society of America and the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America guidelines for developing an institutional program to enhance antimicrobial stewardship. Clin Infect Dis 2007;44:159–177. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
