Predictors of bowel damage in the long-term progression of Crohn's disease
- PMID: 36483818
- PMCID: PMC9724529
- DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i33.12208
Predictors of bowel damage in the long-term progression of Crohn's disease
Abstract
Background: Crohn's disease (CD) is a chronic inflammatory bowel disorder that progresses to bowel damage (BD) over time. An image-based index, the Lémann index (LI), has been developed to measure cumulative BD.
Aim: To characterize the long-term progression of BD in CD based on changes in the LI and to determine risk factors for long-term progression.
Methods: This was a single-center longitudinal cohort study. Patients who had participated in prospective studies on the accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging using endoscopy as a gold standard and who had a follow-up of at least 5 years were re-evaluated after 5-12 years.
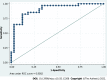
Results: Seventy-two patients were included. LI increased in 38 patients (52.8%), remained unchanged in 9 patients (12.5%), and decreased in 25 patients (34.7%). The small bowel score and surgery subscale significantly increased (P = 0.002 and P = 0.001, respectively), whereas the fistulizing subscale significantly decreased (P = 0.001). Baseline parameters associated with BD progression were ileal location (P = 0.026), CD phenotype [stricturing, fistulizing, or both (P = 0.007, P = 0.006, and P = 0.035, respectively)], disease duration > 10 years (P = 0.019), and baseline LI stricturing score (P = 0.049). No correlation was observed between BD progression and baseline clinical activity, biological markers, or severity of endoscopic lesions.
Conclusion: BD, as assessed by the LI, progressed in half of the patients with CD over a period of 5-12 years. The main determinants of BD progression were ileal location, stricturing/fistulizing phenotype, and disease duration.
Keywords: Bowel damage; Crohn’s disease; Inflammatory bowel disease; Lémann index; Magnetic resonance imaging.
©The Author(s) 2022. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: Dr. Rimola reports grants from Abbvie, personal fees from Alimentiv, personal fees from Janssen, personal fees from Takeda, non-financial support from Gilead and from Agumab during the conduct of the study.
Figures
References
-
- Pariente B, Mary JY, Danese S, Chowers Y, De Cruz P, D’Haens G. Development of the Lémann index to assess digestive tract damage in patients with Crohn’s disease. Gastroenterology. 2015 - PubMed
-
- Van Assche G, Dignass A, Panes J, Beaugerie L, Karagiannis J, Allez M. The second European evidence-based Consensus on the diagnosis and management of Crohn’s disease: Definitions and diagnosis. J Crohn’s Colitis. 2010 - PubMed
-
- Lauriot dit Prevost C, Azahaf M, Nachury M, Branche J, Gerard R, Wils P. Bowel damage and disability in Crohn’s disease: a prospective study in a tertiary referral centre of the Lémann Index and Inflammatory Bowel Disease Disability Index. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2020 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

