Protective effect of recombinant human brain natriuretic peptide against contrast-induced nephropathy in elderly acute myocardial infarction patients: A randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 36483837
- PMCID: PMC9724537
- DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i33.12221
Protective effect of recombinant human brain natriuretic peptide against contrast-induced nephropathy in elderly acute myocardial infarction patients: A randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Increasing reports have demonstrated that recombinant human brain natriuretic peptide (rhBNP) can improve acute myocardial infarction (AMI) and heart failure. However, whether it can improve renal function and decrease the risk of contrast-induced nephropathy (CIN) in elderly AMI patients is still unclear.
Aim: To explore the effect of rhBNP on CIN in elderly AMI patients after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
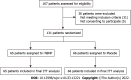
Methods: One hundred and thirty-one elderly AMI patients underwent PCI from January 2017 to July 2021. Patients were either given 1 mL of 0.9% normal saline/(kg/h) for 72 h after PCI (control group, n = 66) and or intravenous rhBNP [1.5 mg/kg followed by 0.0075 mg/(kg/min)] for 72 h (rhBNP treatment group, n = 65). Serum creatinine and cystatin C levels, creatinine clearance rate, and eGFR were measured at 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h after PCI. Research nurses collected data on handwritten forms, and then stored them in password-protected electronic databases.
Results: The creatinine clearance rate and eGFR were increased, while the creatinine and cystatin C levels were decreased significantly in the rhBNP treatment group compared to the control group at 48 h and 72 h. The incidence of CIN (P = 0.028) and acute heart failure (P = 0.017) also significantly decreased in the rhBNP group. No significant difference was noted between the two groups in cardiac death and recurrent AMI.
Conclusion: Early application of rhBNP could protect renal function and decrease the incidence of CIN after primary PCI and acute heart failure.
Keywords: Acute myocardial infarction; Contrast media; Myocardial infarction; Natriuretic peptide; Percutaneous coronary intervention.
©The Author(s) 2022. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare that there are no conflicting interests to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of rhBNP on renal function in STEMI-HF patients with mild renal insufficiency undergoing primary PCI.Heart Vessels. 2016 Apr;31(4):490-8. doi: 10.1007/s00380-015-0642-8. Epub 2015 Jan 31. Heart Vessels. 2016. PMID: 25637044 Clinical Trial.
-
B-type natriuretic peptide for prevention of contrast-induced nephropathy in patients with heart failure undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention.Acta Radiol. 2010 Jul;51(6):641-8. doi: 10.3109/02841851.2010.486804. Acta Radiol. 2010. PMID: 20438292 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of recombinant human brain natriuretic peptide on the prognosis of patients with acute anterior myocardial infarction undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention: a prospective, multi-center, randomized clinical trial.J Thorac Dis. 2017 Jan;9(1):54-63. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2017.01.15. J Thorac Dis. 2017. PMID: 28203406 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of recombinant human brain natriuretic peptide in patients with acute myocardial infarction undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Mar;99(11):e19479. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000019479. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32176080 Free PMC article.
-
A meta-analysis of the clinical efficacy of rhBNP in treating patients with acute myocardial infarction and heart failure.Am J Transl Res. 2021 Apr 15;13(4):2410-2421. eCollection 2021. Am J Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 34017399 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Eindhoven DC, Wu HW, Kremer SWF, van Erkelens JA, Cannegieter SC, Schalij MJ, Borleffs CJW. Mortality differences in acute myocardial infarction patients in the Netherlands: The weekend-effect. Am Heart J. 2018;205:70–76. - PubMed
-
- D'Errigo P, Seccareccia F, Barone AP, Fusco D, Rosato S, Maraschini A, Colais P, Casali G. Effectiveness of invasive reperfusion therapy and standard medical treatment in AMI. Acta Cardiol. 2010;65:645–652. - PubMed
-
- Thiele H, Akin I, Sandri M, Fuernau G, de Waha S, Meyer-Saraei R, Nordbeck P, Geisler T, Landmesser U, Skurk C, Fach A, Lapp H, Piek JJ, Noc M, Goslar T, Felix SB, Maier LS, Stepinska J, Oldroyd K, Serpytis P, Montalescot G, Barthelemy O, Huber K, Windecker S, Savonitto S, Torremante P, Vrints C, Schneider S, Desch S, Zeymer U CULPRIT-SHOCK Investigators. PCI Strategies in Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction and Cardiogenic Shock. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:2419–2432. - PubMed
-
- Lian X, He W, Zhan H, Chen J, Tan N, He P, Liu Y. The effect of trimetazidine on preventing contrast-induced nephropathy after cardiac catheterization. Int Urol Nephrol. 2019;51:2267–2272. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous