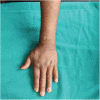
Sporotrichoid lymphocutaneous pattern in a fish-merchant under immunosuppressant medications: Clues to differential diagnoses
- PMID: 36483864
- PMCID: PMC9723480
- DOI: 10.1002/ccr3.6708
Sporotrichoid lymphocutaneous pattern in a fish-merchant under immunosuppressant medications: Clues to differential diagnoses
Abstract
Sporotrichoid-lymphocutaneous-pattern is classically seen in sporotrichosis, though also present in other infections like atypical mycobacteriosis and leishmaniasis. Cutaneous atypical mycobacterial infection presents as localized lesions in immunocompetent and is widespread in immunosuppressed patients. Here, we present a case of sporotrichoid-lymphocutaneous infection due to atypical mycobacteria, in a fish-seller under immunosuppressants.
Keywords: Mycobacterium marinum; Sporotrichoid; atypical mycobacterium; lymphocutaneous pattern.
© 2022 The Authors. Clinical Case Reports published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nodular Lymphangitis (Sporotrichoid Lymphocutaneous Infections). Clues to Differential Diagnosis.J Fungi (Basel). 2018 May 9;4(2):56. doi: 10.3390/jof4020056. J Fungi (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29747448 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sporotrichoid pattern of nerve abscesses in borderline tuberculoid leprosy: A Case Report (sporotrichoid like abscesses in leprosy).Indian J Lepr. 2014 Oct-Dec;86(4):161-3. Indian J Lepr. 2014. PMID: 26411249
-
Sporotrichoid lymphocutaneous infections: etiology, diagnosis and therapy.Am Fam Physician. 2001 Jan 15;63(2):326-32. Am Fam Physician. 2001. PMID: 11201697
-
[Sporotrichoid infection with Mycobacterium marinum: successful therapy with oral tetracycline administration].Hautarzt. 2000 May;51(5):349-52. doi: 10.1007/s001050051131. Hautarzt. 2000. PMID: 10875074 German.
-
Scedosporium apiospermum: An unreported cause of fungal sporotrichoid-like lymphocutaneous infection in Australia and review of the literature.Australas J Dermatol. 2015 May;56(2):e39-42. doi: 10.1111/ajd.12119. Epub 2013 Nov 25. Australas J Dermatol. 2015. PMID: 24266687 Review.
Cited by
-
A Rapid PCR-Based Diagnostic Method for Skin Infection with Mycobacterium marinum.Infect Drug Resist. 2024 Jul 9;17:2833-2851. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S463798. eCollection 2024. Infect Drug Resist. 2024. PMID: 39005849 Free PMC article.
-
Cutaneous Infection Caused by Mycobacterium marinum in Thailand: A 14-Year Retrospective Cohort Analysis of Clinical Characteristics, Complication Risks, and Treatment Efficacy.Health Sci Rep. 2025 Jun 18;8(6):e70915. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.70915. eCollection 2025 Jun. Health Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40535516 Free PMC article.
-
Acid-fast bacteria as causative agents of skin and soft tissue infections: case presentations and literature review.Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 2023 Apr 14;65:e29. doi: 10.1590/S1678-9946202365029. eCollection 2023. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 2023. PMID: 37075336 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aubry A, Chosidow O, Caumes E, Robert J, Cambau E. Sixty‐three cases of Mycobacterium marinum infection: clinical features, treatment, and antibiotic susceptibility of causative isolates. Arch Intern Med. 2002;162(15):1746‐1752. - PubMed
-
- Rallis E, Koumantaki‐Mathioudaki E. Treatment of Mycobacterium marinum cutaneous infections. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2007;8(17):2965‐2978. - PubMed
-
- Ben M, Saghrouni F, Saadi‐Ben Y, et al. Sporotrichoid cutaneous Leishmaniasis in Central Tunisia: epidemiological and clinical aspects. Leishmaniasis – Trends in Epidemiology, Diagnosis and Treatment. IntechOpen; 2014.
-
- Schwendiman MN, Johnson RP, Henning JS. Subcutaneous nodules with sporotrichoid spread. Dermatol Online J. 2009;15(5):9‐12. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources