MicroRNA in adenoid cystic carcinoma (Review)
- PMID: 36484384
- PMCID: PMC9747198
- DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2022.5465
MicroRNA in adenoid cystic carcinoma (Review)
Abstract
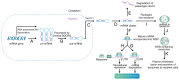
Adenoid cystic carcinoma (ACC) usually arises in the salivary glands, and is a rare tumor, accounting for 1% of all head and neck cancer cases. According to estimates, there are 3‑4.5 cases of ACC for every one million individuals. Numerous studies have reported the association between ACC and microRNAs (miRNAs/miRs). miRNAs are endogenous, non‑coding small RNAs, 19‑25 nt in length, that can regulate target gene expression at the post‑transcriptional level. The aberrant expression of miRNAs may be associated with the prognosis and treatment of patients, as well as with tumorigenesis and tumor development. miRNAs are becoming reliable biomarkers for disease detection due to their varied characteristics, and miRNA target‑based therapies are increasingly being used in clinical practice. The present review provides a brief introduction to ACC and the biogenesis of miRNAs. A summary of the miRNAs that have been validated by in vitro or in vivo studies is then presented, describing their role in ACC.
Keywords: adenoid cystic carcinoma; biomarker; miRNA; pathogenesis; therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Nightingale J, Lum B, Ladwa R, Simpson F, Panizza B. Adenoid cystic carcinoma: A review of clinical features, treatment targets and advances in improving the immune response to monoclonal antibody therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021;1875:188523. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2021.188523. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
