Reduction of cardiac adipose tissue volume with short-term empagliflozin treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes: A substudy from the SIMPLE randomized clinical trial
- PMID: 36484428
- PMCID: PMC10107109
- DOI: 10.1111/dom.14933
Reduction of cardiac adipose tissue volume with short-term empagliflozin treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes: A substudy from the SIMPLE randomized clinical trial
Abstract
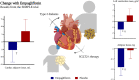
Objective: Ectopic accumulation of cardiac adipose tissue volume (CAT) has been associated with cardiac remodelling and cardiac dysfunction in type 2 diabetes and may be a future therapeutic target. In this substudy from the SIMPLE-trial, we investigated short-term empagliflozin therapy's effects on CAT in patients with type 2 diabetes.
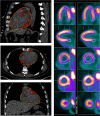
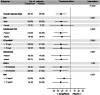
Research design and methods: Between 4 April 2017 and 11 May 2020, we randomized 90 patients with type 2 diabetes and established or high risk of cardiovascular disease to 25 mg empagliflozin or placebo for 13 weeks. The substudy focused on change in CAT evaluated by images acquired during 82 Rubidium-positron emissions tomography/computed tomography. The analysis included 78 patients who had at least one scan. Furthermore, we report on the relation to the concurrent effects on left ventricular mass, end-diastolic volume and end-systolic volume, body composition and glucometabolic status.
Results: Mean ± SD baseline CAT was 258.5 ± 117.9 ml. Empagliflozin reduced CAT after 13 weeks by 12.41 ml [95% CI (-23.83 to -0.99), p = .034] as compared with placebo. Similarly, left ventricular mass [-5.16 g, 95% CI (-8.80 to -1.52), p = .006], end-diastolic volume and end-systolic volume decreased with empagliflozin. In addition, significant improvements were observed in body composition, with reduced total fat mass, and in measures of glucose and lipid metabolism. However, no correlation was observed between changes in CAT and changes in cardiac parameters and change in CAT appeared mediated primarily by concurrent change in weight.
Conclusions: Empagliflozin provides an early reduction of CAT; however, no association was observed with concurrent changes in cardiac volumetrics.
Keywords: cardiac adipose tissue; empagliflozin; metabolism; type 2 diabetes.
© 2022 The Authors. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
CK has served on scientific advisory panels and received speaker fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, Merck Shape and Dome, Astra Zeneca, Amgen, Novartis, Novo Nordisk and Shire. PR has received consultancy and/or speaking fees (to his institution) from Astellas, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Gilead, Novo Nordisk and Sanofi Aventis and research grants from AstraZeneca and Novo Nordisk. MS has received lecture fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, Novo Nordisk, Novartis and Astra Zeneca. SEI has participated on clinical trial executive/steering/publications committees and/or served as an advisor for Boehringer Ingelheim, AstraZeneca, Novo Nordisk, Lexicon, Merck, Pfizer, Abbott, vTv Therapeutics and Esperion. He has delivered lectures supported by Boehringer Ingelheim and AstraZeneca. The remaining authors declare that they have no additional competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Empagliflozin does not change cardiac index nor systemic vascular resistance but rapidly improves left ventricular filling pressure in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled study.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021 Jan 7;20(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s12933-020-01175-5. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021. PMID: 33413355 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Associations of Empagliflozin With Left Ventricular Volumes, Mass, and Function in Patients With Heart Failure and Reduced Ejection Fraction: A Substudy of the Empire HF Randomized Clinical Trial.JAMA Cardiol. 2021 Jul 1;6(7):836-840. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.6827. JAMA Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 33404637 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of Empagliflozin on Left Ventricular Mass in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Coronary Artery Disease: The EMPA-HEART CardioLink-6 Randomized Clinical Trial.Circulation. 2019 Nov 19;140(21):1693-1702. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.042375. Epub 2019 Aug 22. Circulation. 2019. PMID: 31434508 Clinical Trial.
-
Empagliflozin reduces blood pressure and uric acid in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Hum Hypertens. 2019 Apr;33(4):327-339. doi: 10.1038/s41371-018-0134-2. Epub 2018 Nov 15. J Hum Hypertens. 2019. PMID: 30443007
-
Effect of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors on cardiac remodelling: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2022 Feb 3;28(17):1961-1973. doi: 10.1093/eurjpc/zwab173. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2022. PMID: 34792124
Cited by
-
The Effects of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors on Body Composition in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Narrative Review.Diabetes Ther. 2023 Dec;14(12):2015-2030. doi: 10.1007/s13300-023-01481-7. Epub 2023 Oct 14. Diabetes Ther. 2023. PMID: 37837581 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Complex actions of sodium glucose transporter-2 inhibitors on lipids, calcific atherosclerosis, and bone density.Curr Opin Lipidol. 2024 Oct 1;35(5):253-257. doi: 10.1097/MOL.0000000000000942. Epub 2024 Jul 18. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2024. PMID: 39052539 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

