Development of a set of patient reported outcome measures for patients with benign liver tumours and cysts: patient focus groups and systematic review
- PMID: 36484883
- PMCID: PMC9733760
- DOI: 10.1186/s41687-022-00531-1
Development of a set of patient reported outcome measures for patients with benign liver tumours and cysts: patient focus groups and systematic review
Abstract
Background: Patient reported outcome measures (PROMs) may be useful for patients with benign liver tumours and cysts (BLTC) to evaluate the impact of treatment and/or guide shared decision making. Yet, a set of PROMs relevant to patients with BLTC is currently unavailable. In this study, we selected a PROMs set for patients with BLTC.
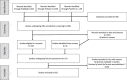
Methods: Potentially relevant patient reported outcomes (PROs) were selected by psychologist-researchers based on keywords used or suggested by participants of two virtual focus groups meetings consisting of thirteen female BLTC patients with a median age of 50 years. Subsequently, patients were asked to report their most relevant PROs. PROMs identified by systematic literature review and computerized adaptive tests (CATs) in the Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System (PROMIS) were considered in selecting the final PROMs set to assess relevant outcomes.
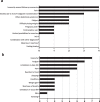
Results: The most important PROs were: insecurity/anxiety (11/12 patients), pain (9/12 patients), fatigue (8/12 patients), and limitations in daily life (5/12 patients). The literature review included 23 studies, which used various generic and disease-specific PROMs, often not measuring (all) relevant PROs. The final selected PROMs set included numerical rating scales for pain, two questions on overall health and quality of life and four PROMIS CATs.
Conclusions: A PROMs set generically and efficiently measuring outcomes relevant for patients with BLTC was developed and may be used in future research and clinical practice.
Keywords: Benign liver tumours; Patient reported outcomes; Symptoms.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Patient-reported outcomes for people with diabetes: what and how to measure? A narrative review.Diabetologia. 2023 Aug;66(8):1357-1377. doi: 10.1007/s00125-023-05926-3. Epub 2023 May 24. Diabetologia. 2023. PMID: 37222772 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of a standard set of PROs and generic PROMs for Dutch medical specialist care : Recommendations from the Outcome-Based Healthcare Program Working Group Generic PROMs.Qual Life Res. 2023 Jun;32(6):1595-1605. doi: 10.1007/s11136-022-03328-3. Epub 2023 Feb 9. Qual Life Res. 2023. PMID: 36757571 Free PMC article.
-
Common patient-reported outcomes across ICHOM Standard Sets: the potential contribution of PROMIS®.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2021 Sep 6;21(1):259. doi: 10.1186/s12911-021-01624-5. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2021. PMID: 34488730 Free PMC article.
-
Implementing patient-reported outcomes in clinical decision-making within knee and hip osteoarthritis: an explorative review.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019 May 17;20(1):230. doi: 10.1186/s12891-019-2620-2. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019. PMID: 31101042 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Study protocol for a multicentre nationwide prospective cohort study to investigate the natural course and clinical outcome in benign liver tumours and cysts in the Netherlands: the BELIVER study.BMJ Open. 2022 Sep 8;12(9):e055104. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-055104. BMJ Open. 2022. PMID: 36691222 Free PMC article.
References
-
- European Association for the Study of the Liver (2016) EASL clinical practice guidelines on the management of benign liver tumours. J Hepatol 65(2):386–398 - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

