The pattern and magnitude of T cell subsets reconstitution during ten years of ART with viral suppression in HIV-infected patients
- PMID: 36490352
- PMCID: PMC9792206
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.204416
The pattern and magnitude of T cell subsets reconstitution during ten years of ART with viral suppression in HIV-infected patients
Abstract
Background: The extent of immune reconstitution in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infected persons receiving long-term antiretroviral therapy (ART) with controlled viral load has been controversial. We studied the extent and speed of T cell subsets retrieval after long-term antiretroviral treatment.
Methods: 662 HIV-infected patients followed at least 2 years whose plasma HIV-1 RNA load <50 copies/mL were evaluated for longitudinal and functional phenotypic indices of immune restoration. Determinants of change in magnitude and importance of recovery have been evaluated using mixed linear regression models.
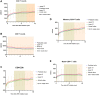
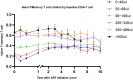
Results: Almost all robust immune restorations achieved occurred after 2-3 years of ART. The median CD4 lymphocyte count increased 449 cells/μl (IQR 303-604) from 226 cells/μl (IQR 83-336) at baseline during the third year (P < 0.001); CD4+T lymphocyte rises during the sixth and tenth years were not significant. Naive and memory CD4+T cells'reconstitution occurred in the sixth and eighth years of ART but no significant change thereafter. The change of CD45RA+Naïve and CD45RA-memory CD4+T cell reconstitution is different in baseline CD4+T cell counts <100 cells/μl group and in baseline CD4+T cell counts >100 cells/μl group. Activation antigen expression (CD38 or HLA-DR) on CD8 lymphocytes declined mostly during the first till second year, and after 4 years, activation antigen expression on patient lymphocytes showed no significant change. The proportion of CD4 cells expressing CD28 climbed during the first years and reached normal levels in the second year.
Conclusions: Immune restoration was dependent on the capacity of immune system during the first 2-3 year of ART. But the significant change of CD4 and compartments of CD4+T cells could persist until 6-8 years. The pattern of CD38+CD8+, HLA-DR+CD8+, CD28+CD4+ T cells could quickly return to normal level and no significant change after sufficient time of ART. In general, the immune response compared to the baseline status may be the overall effect from the age and time of antiretroviral treatment.
Keywords: CD4+T cell; CD4/CD8; HIV; T cell subsets; antiretroviral treatment; immune reconstitution.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Characterizing the immune system after long-term undetectable viral load in HIV-1-infected children.J Clin Immunol. 2003 Jul;23(4):279-89. doi: 10.1023/a:1024536816684. J Clin Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12959220
-
Changes in CD4+ and CD8+ T cell subsets in response to highly active antiretroviral therapy in HIV type 1-infected patients with prior protease inhibitor experience.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1998 May 1;14(7):561-9. doi: 10.1089/aid.1998.14.561. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1998. PMID: 9591710
-
Immunological benefits of antiretroviral therapy in very early stages of asymptomatic chronic HIV-1 infection.AIDS. 2000 Sep 8;14(13):1921-33. doi: 10.1097/00002030-200009080-00007. AIDS. 2000. PMID: 10997396 Clinical Trial.
-
Recovery of the immune system with antiretroviral therapy: the end of opportunism?JAMA. 1998 Jul 1;280(1):72-7. doi: 10.1001/jama.280.1.72. JAMA. 1998. PMID: 9660367
-
Cellular and molecular insights into incomplete immune recovery in HIV/AIDS patients.Front Immunol. 2023 May 2;14:1152951. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1152951. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37205108 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Grand Challenges on HIV/AIDS in China - The 5th Symposium, Yunnan 2024.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2025 Dec;14(1):2492208. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2025.2492208. Epub 2025 Apr 22. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2025. PMID: 40202047 Free PMC article.
-
Dominant CD4+ T cell receptors remain stable throughout antiretroviral therapy-mediated immune restoration in people with HIV.Cell Rep Med. 2023 Nov 21;4(11):101268. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2023.101268. Epub 2023 Nov 9. Cell Rep Med. 2023. PMID: 37949070 Free PMC article.
-
CD4+ T cell counts and soluble programmed death-1 at baseline correlated with hepatitis B surface antigen decline in HIV/HBV coinfection during combined antiretroviral therapy.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 May 3;13:1178788. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1178788. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37207191 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment and evaluation of a predictive model for immune reconstitution in people living with HIV after antiretroviral therapy.BMC Infect Dis. 2025 Feb 24;25(1):264. doi: 10.1186/s12879-025-10673-4. BMC Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 39994545 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial antigen-presenting cell system reveals CD28's role in modulating T cell functions during human immunodeficiency virus infection.iScience. 2024 Sep 13;27(10):110947. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110947. eCollection 2024 Oct 18. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39381752 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO. Global HIV and AIDS statistics - 2019 fact sheet. 2020. https://www.who.int/teams/global-hiv-hepatitis-and-stis-programmes/hiv/s....
-
- Evans TG, Bonnez W, Soucier HR, Fitzgerald T, Gibbons DC, Reichman RC. Highly active antiretroviral therapy results in a decrease in CD8+ T cell activation and preferential reconstitution of the peripheral CD4+ T cell population with memory rather than naive cells. Antiviral Res. 1998; 39:163–73. 10.1016/s0166-3542(98)00035-7 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

