Cov2MS: An Automated and Quantitative Matrix-Independent Assay for Mass Spectrometric Measurement of SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein
- PMID: 36490367
- PMCID: PMC9773173
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.2c01610
Cov2MS: An Automated and Quantitative Matrix-Independent Assay for Mass Spectrometric Measurement of SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein
Abstract
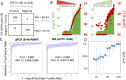
The pandemic readiness toolbox needs to be extended, targeting different biomolecules, using orthogonal experimental set-ups. Here, we build on our Cov-MS effort using LC-MS, adding SISCAPA technology to enrich proteotypic peptides of the SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid (N) protein from trypsin-digested patient samples. The Cov2MS assay is compatible with most matrices including nasopharyngeal swabs, saliva, and plasma and has increased sensitivity into the attomole range, a 1000-fold improvement compared to direct detection in a matrix. A strong positive correlation was observed with qPCR detection beyond a quantification cycle of 30-31, the level where no live virus can be cultured. The automatable sample preparation and reduced LC dependency allow analysis of up to 500 samples per day per instrument. Importantly, peptide enrichment allows detection of the N protein in pooled samples without sensitivity loss. Easily multiplexed, we detect variants and propose targets for Influenza A and B detection. Thus, the Cov2MS assay can be adapted to test for many different pathogens in pooled samples, providing longitudinal epidemiological monitoring of large numbers of pathogens within a population as an early warning system.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): Van Oudenhove L., Claereboudt J., Wardle R., Foley D., Wyndham K, and Vissers J.P.C. are employed by Waters Corporation. Razavi M., Yip Y., Pearson TW. and Anderson N.L. are employed by SISCAPA Assay Technologies Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Bruce E. A.; Mills M. G.; Sampoleo R.; Perchetti G. A.; Huang M.; Despres H. W.; Schmidt M. M.; Roychoudhury P.; Shirley D. J.; Jerome K. R.; Greninger A. L.; Botten J. W. Predicting Infectivity: Comparing Four PCR-based Assays to Detect Culturable SARS-CoV-2 in Clinical Samples. EMBO Mol. Med. 2022, 14, e1529010.15252/EMMM.202115290. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pinto G.; Illiano A.; Ferrucci V.; Quarantelli F.; Fontanarosa C.; Siciliano R.; Di Domenico C.; Izzo B.; Pucci P.; Marino G.; Zollo M.; Amoresano A. Identification of SARS-CoV-2 Proteins from Nasopharyngeal Swabs Probed by Multiple Reaction Monitoring Tandem Mass Spectrometry. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 34945–34953. 10.1021/ACSOMEGA.1C05587. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cardozo K. H. M.; Lebkuchen A.; Okai G. G.; Schuch R. A.; Viana L. G.; Olive A. N.; dos Santos Lazari C.; Fraga A. M.; Granato C. F. H.; Pintão M. C. T.; Carvalho V. M. Establishing a Mass Spectrometry-Based System for Rapid Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in Large Clinical Sample Cohorts. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6201.10.1038/s41467-020-19925-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

