Canonical NF-κB signaling pathway and GRO-α/CXCR2 axis are activated in unruptured intracranial aneurysm patients
- PMID: 36494512
- PMCID: PMC9734124
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-25855-2
Canonical NF-κB signaling pathway and GRO-α/CXCR2 axis are activated in unruptured intracranial aneurysm patients
Abstract
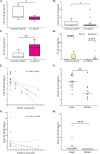
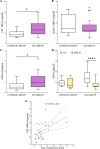
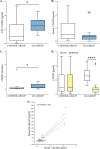
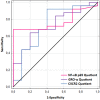
Activation of the nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) stimulates the production of pro-inflammatory molecules involved in the formation of intracranial aneurysms (IA). The study aimed to assess the NF-κB p65 subunit and the GRO-α chemokine and its receptor CXCR2 concentrations in unruptured intracranial aneurysm patients (UIA, n = 25) compared to individuals without vascular changes in the brain (n = 10). It was also analyzed whether tested proteins are related to the size and number of aneurysms. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and serum protein levels were measured using the ELISA method. Median CSF and serum NF-κB p65 concentrations were significantly lower, while median CSF GRO-α and CXCR2 concentrations were significantly higher in UIA patients compared to the control group. CSF and serum NF-κB p65 concentrations negatively correlated with the number of aneurysms. In UIA patients the median GRO-α concentration was two-fold and CXCR2 almost four-fold higher in CSF compared to the serum value. CSF GRO-α concentration positively correlated with the size of aneurysms.Significantly decreased CSF NF-κB p65 and significantly increased CSF GRO-α and its CXCR2 receptor concentrations in UIA patients compared to the control group may altogether suggest that the canonical NF-κB signaling pathway is activated and its target pro-inflammatory genes are highly expressed in UIA patients. However, to unequivocally assess the involvement of the classical NF-κB pathway with the participation of the NF-κB p65 subunit and the GRO-α/CXCR2 axis in the formation of IA, further in vivo model studies are needed.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The preliminary study suggests an association between NF-ĸB pathway activation and increased plasma 20S proteasome activity in intracranial aneurysm patients.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 16;14(1):3941. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-54692-8. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38366068 Free PMC article.
-
Apc gene suppresses intracranial aneurysm formation and rupture through inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway mediated inflammatory response.Biosci Rep. 2019 Mar 26;39(3):BSR20181909. doi: 10.1042/BSR20181909. Print 2019 Mar 29. Biosci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30808715 Free PMC article.
-
Pro-Inflammatory and Anti-Inflammatory Cytokines Levels are Significantly Altered in Cerebrospinal Fluid of Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysm (UIA) Patients.J Inflamm Res. 2022 Nov 11;15:6245-6261. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S380524. eCollection 2022. J Inflamm Res. 2022. PMID: 36386592 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into ADAMs regulation of the GRO-α/CXCR2 system: focus on Sjögren's syndrome.Int Rev Immunol. 2015;34(6):486-99. doi: 10.3109/08830185.2014.975892. Epub 2014 Nov 11. Int Rev Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25386842 Review.
-
CXCR2 Receptor: Regulation of Expression, Signal Transduction, and Involvement in Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 16;23(4):2168. doi: 10.3390/ijms23042168. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35216283 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Current understanding of macrophages in intracranial aneurysm: relevant etiological manifestations, signaling modulation and therapeutic strategies.Front Immunol. 2024 Jan 8;14:1320098. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1320098. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38259443 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The preliminary study suggests an association between NF-ĸB pathway activation and increased plasma 20S proteasome activity in intracranial aneurysm patients.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 16;14(1):3941. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-54692-8. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38366068 Free PMC article.
-
Intracranial Aneurysm Biomarkers: A Convergence of Genetics, Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and the Extracellular Matrix.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 2;26(7):3316. doi: 10.3390/ijms26073316. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40244203 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating inflammatory biomarkers and risk of intracranial aneurysm: a Mendelian randomization study.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Jan 3;29(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s40001-023-01609-2. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 38173028 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of the Transforming Growth Factor β (TGF-β) on Brain Aneurysm Formation and Development: A Literature Review.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2025 May 20;45(1):46. doi: 10.1007/s10571-025-01572-y. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40392340 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kamińska, J. et al. Ratio of IL-8 in CSF versus serum is elevated in patients with unruptured brain aneurysm. J. Clin. Med. 9 (6), 1761 https://www.mdpi.com/2077-0383/9/6/1761 (2020). - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

