Implementation of a low-titre whole blood transfusion program in a civilian helicopter emergency medical service
- PMID: 36494743
- PMCID: PMC9733220
- DOI: 10.1186/s13049-022-01051-z
Implementation of a low-titre whole blood transfusion program in a civilian helicopter emergency medical service
Abstract
Background: Early balanced transfusion is associated with improved outcome in haemorrhagic shock patients. This study describes the implementation and evaluates the safety of a whole blood transfusion program in a civilian helicopter emergency medical service (HEMS).
Methods: This prospective observational study was performed over a 5-year period at HEMS-Bergen, Norway. Patients in haemorrhagic shock receiving out of hospital transfusion of low-titre Group O whole blood (LTOWB) or other blood components were included. Two LTOWB units were produced weekly and rotated to the HEMS for forward storage. The primary endpoints were the number of patients transfused, mechanisms of injury/illness, adverse events and survival rates. Informed consent covered patient pathway from time of emergency interventions to last endpoint and subsequent data handling/storage.
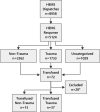
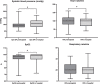
Results: The HEMS responded to 5124 patients. Seventy-two (1.4%) patients received transfusions. Twenty patients (28%) were excluded due to lack of consent (16) or not meeting the inclusion criteria (4). Of the 52 (100%) patients, 48 (92%) received LTOWB, nine (17%) received packed red blood cells (PRBC), and nine (17%) received freeze-dried plasma. Of the forty-six (88%) patients admitted alive to hospital, 35 (76%) received additional blood transfusions during the first 24 h. Categories were blunt trauma 30 (58%), penetrating trauma 7 (13%), and nontrauma 15 (29%). The majority (79%) were male, with a median age of 49 (IQR 27-70) years. No transfusion reactions, serious complications or logistical challenges were reported. Overall, 36 (69%) patients survived 24 h, and 28 (54%) survived 30 days.
Conclusions: Implementing a whole blood transfusion program in civilian HEMS is feasible and safe and the logistics around out of hospital whole blood transfusions are manageable. Trial registration The study is registered in the ClinicalTrials.gov registry (NCT02784951).
Keywords: Blood transfusion; Haemorrhagic shock; Helicopter Emergency Medical Services; Low-titre group O whole blood; Out of hospital.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Crombie N, Doughty HA, Bishop JRB, Desai A, Dixon EF, Hancox JM, et al. Resuscitation with blood products in patients with trauma-related haemorrhagic shock receiving prehospital care (RePHILL): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2022;9:e250–e261. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(22)00040-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shackelford SA, Del Junco DJ, Powell-Dunford N, Mazuchowski EL, Howard JT, Kotwal RS, et al. Association of prehospital blood product transfusion during medical evacuation of combat casualties in afghanistan with acute and 30-day survival. JAMA. 2017;318(16):1581–1591. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.15097. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

