Optimal transport features for morphometric population analysis
- PMID: 36495600
- PMCID: PMC9829456
- DOI: 10.1016/j.media.2022.102696
Optimal transport features for morphometric population analysis
Abstract
Brain pathologies often manifest as partial or complete loss of tissue. The goal of many neuroimaging studies is to capture the location and amount of tissue changes with respect to a clinical variable of interest, such as disease progression. Morphometric analysis approaches capture local differences in the distribution of tissue or other quantities of interest in relation to a clinical variable. We propose to augment morphometric analysis with an additional feature extraction step based on unbalanced optimal transport. The optimal transport feature extraction step increases statistical power for pathologies that cause spatially dispersed tissue loss, minimizes sensitivity to shifts due to spatial misalignment or differences in brain topology, and separates changes due to volume differences from changes due to tissue location. We demonstrate the proposed optimal transport feature extraction step in the context of a volumetric morphometric analysis of the OASIS-1 study for Alzheimer's disease. The results demonstrate that the proposed approach can identify tissue changes and differences that are not otherwise measurable.
Keywords: MRI; Morphometry; Optimal transport; Optimization; Population analysis.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
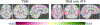

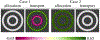




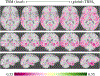

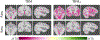

References
-
- Ahuja RK, Magnanti TL, Orlin JB, 1993. Network Flows: Theory, Algorithms, and Applications. Prentice-Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA.
-
- Anderes E, Borgwardt S, Miller J, 2016. Discrete wasserstein barycenters: Optimal transport for discrete data. Mathematical Methods of Operations Research 84, 389–409.
-
- Ashburner J, 2007. A fast diffeomorphic image registration algorithm. Neuroimage 38, 95–113. - PubMed
-
- Ashburner J, Friston KJ, 2000. Voxel-based morphometry—the methods. Neuroimage 11, 805–821. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

