Regulation of eukaryotic protein kinases by Pin1, a peptidyl-prolyl isomerase
- PMID: 36496344
- PMCID: PMC9992314
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbior.2022.100938
Regulation of eukaryotic protein kinases by Pin1, a peptidyl-prolyl isomerase
Abstract
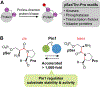
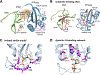
The peptidyl-prolyl isomerase Pin1 cooperates with proline-directed kinases and phosphatases to regulate multiple oncogenic pathways. Pin1 specifically recognizes phosphorylated Ser/Thr-Pro motifs in proteins and catalyzes their cis-trans isomerization. The Pin1-catalyzed conformational changes determine the stability, activity, and subcellular localization of numerous protein substrates. We conducted a survey of eukaryotic protein kinases that are regulated by Pin1 and whose Pin1 binding sites have been identified. Our analyses reveal that Pin1 target sites in kinases do not fall exclusively within the intrinsically disordered regions of these enzymes. Rather, they fall into three groups based on their location: (i) within the catalytic kinase domain, (ii) in the C-terminal kinase region, and (iii) in regulatory domains. Some of the kinases downregulated by Pin1 activity are tumor-suppressing, and all kinases upregulated by Pin1 activity are functionally pro-oncogenic. These findings further reinforce the rationale for developing Pin1-specific inhibitors as attractive pharmaceuticals for cancer therapy.
Keywords: Cis-trans isomerization; Eukaryotic protein kinase; Oncogenic pathway; Peptidyl-prolyl isomerase Pin1; Proline-directed protein kinase; Tumor suppressor.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
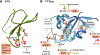

Similar articles
-
Phosphorylation-dependent prolyl isomerization: a novel signaling regulatory mechanism.Cell Mol Life Sci. 1999 Nov 30;56(9-10):788-806. doi: 10.1007/s000180050026. Cell Mol Life Sci. 1999. PMID: 11212339 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dual Roles of Pin1 in Cancer Development and Progression.Curr Pharm Des. 2017 Nov 16;23(29):4422-4425. doi: 10.2174/1381612823666170703164711. Curr Pharm Des. 2017. PMID: 28671058 Review.
-
A tethering mechanism underlies Pin1-catalyzed proline cis-trans isomerization at a noncanonical site.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 May 27;122(21):e2414606122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2414606122. Epub 2025 May 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 40388619
-
The Peptidyl-Prolyl cis-trans isomerase, Pin1, associates with Protein Kinase C θ via a critical Phospho-Thr-Pro motif in the V3 regulatory domain.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 8;14:1126464. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1126464. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36969236 Free PMC article.
-
Role of phosphorylation in determining the backbone dynamics of the serine/threonine-proline motif and Pin1 substrate recognition.Biochemistry. 1998 Apr 21;37(16):5566-75. doi: 10.1021/bi973060z. Biochemistry. 1998. PMID: 9548941
Cited by
-
The role of the master cancer regulator Pin1 in the development and treatment of cancer.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Apr 30;12:1343938. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1343938. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 38745861 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel bivalent interaction mode underlies a non-catalytic mechanism for Pin1-mediated protein kinase C regulation.Elife. 2024 Apr 30;13:e92884. doi: 10.7554/eLife.92884. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38687676 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and inhibition of PIN1-NRF2 protein-protein interactions through computational and biophysical approaches.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 14;15(1):8907. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-89342-0. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40087364 Free PMC article.
-
Covalent Inhibition of the Peptidyl-Prolyl Isomerase Pin1 by Sulfopin Results in a Broad Impact on the Phosphoproteome of Human Osteosarcoma U2-OS Cells.Proteomics. 2025 Jul;25(14):e13980. doi: 10.1002/pmic.13980. Epub 2025 Jun 23. Proteomics. 2025. PMID: 40546013 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Althubiti M, Rada M, Samuel J, Escorsa JM, Najeeb H, Lee KG, Lam KP, Jones GD, Barlev NA, Macip S, 2016. BTK Modulates p53 Activity to Enhance Apoptotic and Senescent Responses. Cancer Res 76(18), 5405–5414. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

