A novel autophagy-related long non-coding RNAs prognostic risk score for clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 36496360
- PMCID: PMC9741795
- DOI: 10.1186/s12894-022-01148-8
A novel autophagy-related long non-coding RNAs prognostic risk score for clear cell renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
Background: As the main histological subtype of renal cell carcinoma, clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) places a heavy burden on health worldwide. Autophagy-related long non-coding RNAs (ARlncRs) have shown tremendous potential as prognostic signatures in several studies, but the relationship between them and ccRCC still has to be demonstrated.
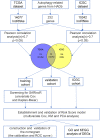
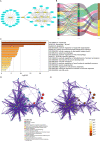
Methods: The RNA-sequencing and clinical characteristics of 483 ccRCC patients were downloaded download from the Cancer Genome Atlas and International Cancer Genome Consortium. ARlncRs were determined by Pearson correlation analysis. Univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses were applied to establish a risk score model. A nomogram was constructed considering independent prognostic factors. The Harrell concordance index calibration curve and the receiver operating characteristic analysis were utilized to evaluate the nomogram. Furthermore, functional enrichment analysis was used for differentially expressed genes between the two groups of high- and low-risk scores.
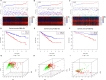
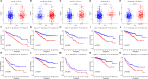
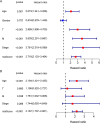
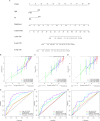
Results: A total of 9 SARlncRs were established as a risk score model. The Kaplan-Meier survival curve, principal component analysis, and subgroup analysis showed that low overall survival of patients was associated with high-risk scores. Age, M stage, and risk score were identified as independent prognostic factors to establish a nomogram, whose concordance index in the training cohort, internal validation, and external ICGC cohort was 0.793, 0.671, and 0.668 respectively. The area under the curve for 5-year OS prediction in the training cohort, internal validation, and external ICGC cohort was 0.840, 0.706, and 0.708, respectively. GO analysis and KEGG analysis of DEGs demonstrated that immune- and inflammatory-related pathways are likely to be critically involved in the progress of ccRCC.
Conclusions: We established and validated a novel ARlncRs prognostic risk model which is valuable as a potential therapeutic target and prognosis indicator for ccRCC. A nomogram including the risk model is a promising clinical tool for outcomes prediction of ccRCC patients and further formulation of individualized strategy.
Keywords: Autophagy; Clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC); Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA); Prognosis; Risk score.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

