Extracellular vesicles from IFN-γ-primed mesenchymal stem cells repress atopic dermatitis in mice
- PMID: 36496385
- PMCID: PMC9741801
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-022-01728-8
Extracellular vesicles from IFN-γ-primed mesenchymal stem cells repress atopic dermatitis in mice
Abstract
Background: Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a chronic inflammatory skin disorder characterized by immune dysregulation, pruritus, and abnormal epidermal barrier function. Compared with conventional mesenchymal stem cell (MSC), induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived mesenchymal stem cell (iMSC) is recognized as a unique source for producing extracellular vesicles (EVs) because it can be obtained in a scalable manner with an enhanced homogeneity. Stimulation of iMSCs with inflammatory cytokines can improve the immune-regulatory, anti-inflammatory, and tissue-repairing potential of iMSC-derived EVs.
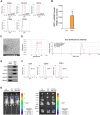
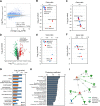
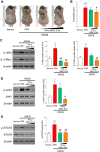
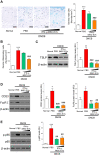
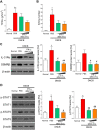
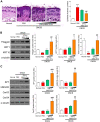
Results: Proteome analysis showed that IFN-γ-iMSC-EVs are enriched with protein sets that are involved in regulating interferon responses and inflammatory pathways. In AD mice, expression of interleukin receptors for Th2 cytokines (IL-4Rα/13Rα1/31Rα) and activation of their corresponding intracellular signaling molecules was reduced. IFN-γ-iMSC-EVs decreased itching, which was supported by reduced inflammatory cell infiltration and mast cells in AD mouse skin; reduced IgE receptor expression and thymic stromal lymphopoietin and NF-kB activation; and recovered impaired skin barrier, as evidenced by upregulation of key genes of epidermal differentiation and lipid synthesis.
Conclusions: IFN-γ-iMSC-EVs inhibit Th2-induced immune responses, suppress inflammation, and facilitate skin barrier restoration, contributing to AD improvement.
Keywords: Atopic dermatitis; Extracellular vesicles; IFN-γ; iPSC-derived MSC.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Soo Kim is the chief executive officer of Brexogen Inc. Other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The application potential of iMSCs and iMSC-EVs in diseases.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Jul 29;12:1434465. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1434465. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39135947 Free PMC article. Review.
-
iMSC-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Improve Atopic Dermatitis by Augmenting Skin Barrier Integrity and Inhibiting Inflammation, Pruritus and Th2 Immune Responses.J Extracell Biol. 2025 Jun 23;4(6):e70067. doi: 10.1002/jex2.70067. eCollection 2025 Jun. J Extracell Biol. 2025. PMID: 40552105 Free PMC article.
-
Exosome from IFN-γ-Primed Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Improved Skin Inflammation and Barrier Function.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 19;24(14):11635. doi: 10.3390/ijms241411635. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37511392 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Canine Adipose Tissue Ameliorates Inflammation, Skin Barrier Function and Pruritus by Reducing JAK/STAT Signaling in Atopic Dermatitis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 27;23(9):4868. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094868. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563259 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in the Management of Atopic Dermatitis: A Scoping Review of Therapeutic Opportunities and Challenges.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Mar 4;20:2673-2693. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S494574. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40061879 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic Efficacy of Interferon-Gamma and Hypoxia-Primed Mesenchymal Stromal Cells and Their Extracellular Vesicles: Underlying Mechanisms and Potentials in Clinical Translation.Biomedicines. 2024 Jun 20;12(6):1369. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12061369. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38927577 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomes and Exosome-Mimetics for Atopic Dermatitis Therapy.Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2025 Jun;22(4):381-396. doi: 10.1007/s13770-024-00695-5. Epub 2025 Jan 20. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2025. PMID: 39832066 Review.
-
The application potential of iMSCs and iMSC-EVs in diseases.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Jul 29;12:1434465. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1434465. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39135947 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic roles of natural and engineered mesenchymal stem cells and extracellular vesicles in atopic dermatitis.Regen Ther. 2025 Jun 4;30:123-135. doi: 10.1016/j.reth.2025.05.009. eCollection 2025 Dec. Regen Ther. 2025. PMID: 40521136 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nitric oxide-primed engineered extracellular vesicles restore bioenergetics in acute kidney injury via mitochondrial transfer.Theranostics. 2025 Apr 13;15(11):5499-5517. doi: 10.7150/thno.113741. eCollection 2025. Theranostics. 2025. PMID: 40303326 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Singh S, Behl T, Sharma N, Zahoor I, Chigurupati S, Yadav S, Rachamalla M, Sehgal A, Naved T, Pritima, et al. Targeting therapeutic approaches and highlighting the potential role of nanotechnology in atopic dermatitis. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022;29:32605–32630. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-18429-8. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

