Pneumococcal concentration and serotype distribution in preschool children with radiologically confirmed pneumonia compared to healthy controls prior to introduction of pneumococcal vaccination in Zanzibar: an observational study
- PMID: 36496395
- PMCID: PMC9737767
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-022-07902-5
Pneumococcal concentration and serotype distribution in preschool children with radiologically confirmed pneumonia compared to healthy controls prior to introduction of pneumococcal vaccination in Zanzibar: an observational study
Abstract
Background: The World Health Organization recommends pneumococcal vaccination (PCV) in the first year of life. We investigated pneumococcal serotypes in children with clinical or radiologically confirmed pneumonia and healthy controls prior to PCV13 vaccine introduction in Zanzibar.
Methods: Children (n = 677) with non-severe acute febrile illness aged 2-59 months presenting to a health centre in Zanzibar, Tanzania April-July 2011 were included. Nasopharyngeal swabs collected at enrolment were analysed by real-time PCR to detect and quantify pneumococcal serotypes in patients (n = 648) and in healthy asymptomatic community controls (n = 161). Children with clinical signs of pneumonia according to the Integrated Management of Childhood illness guidelines ("IMCI pneumonia") were subjected to a chest-X-ray. Consolidation on chest X-ray was considered "radiological pneumonia".
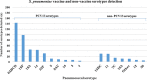
Results: Pneumococcal DNA was detected in the nasopharynx of 562/809 (69%) children (70% in patients and 64% in healthy controls), with no significant difference in proportions between patients with or without presence of fever, malnutrition, IMCI pneumonia or radiological pneumonia. The mean pneumococcal concentration was similar in children with and without radiological pneumonia (Ct value 26.3 versus 27.0, respectively, p = 0.3115). At least one serotype could be determined in 423 (75%) participants positive for pneumococci of which 33% had multiple serotypes detected. A total of 23 different serotypes were identified. One serotype (19F) was more common in children with fever (86/648, 13%) than in healthy controls (12/161, 7%), (p = 0.043). Logistic regression adjusting for age and gender showed that serotype 9A/V [aOR = 10.9 (CI 2.0-60.0, p = 0.006)] and 14 [aOR = 3.9 (CI 1.4-11.0, p = 0.012)] were associated with radiological pneumonia. The serotypes included in the PCV13 vaccine were found in 376 (89%) of the 423 serotype positive participants.
Conclusion: The PCV13 vaccine introduced in 2012 targets a great majority of the identified serotypes. Infections with multiple serotypes are common. PCR-determined concentrations of pneumococci in nasopharynx were not associated with radiologically confirmed pneumonia. Trial registration Clinicaltrials.gov (NCT01094431).
Keywords: Antibiotics; Immunization; Pneumococci; Pneumonia; Preschool child; Radiology; Serotypes; Sub-Saharan Africa.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effectiveness of Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccines Against Community-acquired Alveolar Pneumonia Attributable to Vaccine-serotype Streptococcus pneumoniae Among Children.Clin Infect Dis. 2021 Oct 5;73(7):e1423-e1433. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa1860. Clin Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 33346348 Free PMC article.
-
Nasopharyngeal carriage of Streptococcus pneumoniae serotypes among children in India prior to the introduction of pneumococcal conjugate vaccines: a cross-sectional study.BMC Infect Dis. 2019 Jul 10;19(1):605. doi: 10.1186/s12879-019-4254-2. BMC Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 31291902 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of pneumococcal nasopharyngeal colonization and serotypes circulating in Cameroonian children after the 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine introduction.Int J Infect Dis. 2020 Sep;98:113-120. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.06.048. Epub 2020 Jun 17. Int J Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32562849
-
Estimating the impact of pneumococcal conjugate vaccines on childhood pneumonia in sub-Saharan Africa: A systematic review.F1000Res. 2020 Jul 23;9:765. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.25227.2. eCollection 2020. F1000Res. 2020. PMID: 33335713 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive review of safety in Experimental Human Pneumococcal Challenge.PLoS One. 2023 May 4;18(5):e0284399. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0284399. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37141259 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Radiographically confirmed pneumonia in Malawian children and associated pneumococcal carriage after introduction of the 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine.Pneumonia (Nathan). 2024 Oct 5;16(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s41479-024-00147-7. Pneumonia (Nathan). 2024. PMID: 39367515 Free PMC article.
-
Co-occurrence of bacteria and viruses and serotype distribution of Streptococcus pneumoniae in the nasopharynx of Tanzanian children below 2 years of age following introduction of the PCV13.Front Public Health. 2024 Jan 22;12:1298222. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1298222. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38317802 Free PMC article.
-
Current challenges and new approaches to implementing optimal management of sickle cell disease in sub-Saharan Africa.Semin Hematol. 2023 Sep;60(4):192-199. doi: 10.1053/j.seminhematol.2023.08.002. Epub 2023 Aug 24. Semin Hematol. 2023. PMID: 37730472 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wahl B, O'Brien KL, Greenbaum A, Majumder A, Liu L, Chu Y, et al. Burden of Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae type b disease in children in the era of conjugate vaccines: global, regional, and national estimates for 2000–15. Lancet Glob Health. 2018;6(7):e744–e757. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(18)30247-X. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Collaborators GBDLRI Estimates of the global, regional, and national morbidity, mortality, and aetiologies of lower respiratory infections in 195 countries, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Infect Dis. 2018;18(11):1191–1210. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30310-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Heinsbroek E, Tafatatha T, Phiri A, Swarthout TD, Alaerts M, Crampin AC, et al. Pneumococcal carriage in households in Karonga District, Malawi, before and after introduction of 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccination. Vaccine. 2018;36(48):7369–7376. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2018.10.021. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous