Enhanced Functionality and Bio-Accessibility of Composite Pomegranate Peel Extract-Enriched "Boba Balls"
- PMID: 36496593
- PMCID: PMC9739420
- DOI: 10.3390/foods11233785
Enhanced Functionality and Bio-Accessibility of Composite Pomegranate Peel Extract-Enriched "Boba Balls"
Abstract
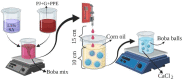
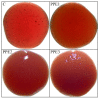
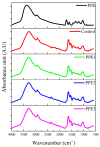
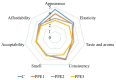
“Boba balls” or pearls have recently gained popularity for beverages or food toppings. “Boba balls” could be developed into functional foods by the encapsulation of bioactive compounds. In this study, gelatin/sodium alginate composite “Boba balls” enriched with pomegranate peel extract (PPE) at different concentrations (0, 1, 2, and 3%) were prepared. They were characterized in terms of physical, rheological, textural, morphological, and sensory properties, as well as in vitro digestion, bio-accessibility, and release kinetic of PPE. Adding PPE improved the “Boba” mix’s viscoelasticity and decreased the “Boba balls”’ hardness. The increasing PPE ratio significantly (p < 0.05) increased the antioxidant capacity and total phenolic content. The addition of PPE preserved the spherical shape of the “Boba balls”, and as the PPE ratio increased, new junction zones were observed in SEM images. The in vitro digestibility of PPE was significantly (p < 0.05) improved by preserving PPE from the mouth and gastric medium, and “Boba balls” showed the highest release and bio-accessibility in the intestinal medium. Consequently, PPE as a by-product could be successfully used at 2% concentration for enhancing the functionality and bio-accessibility of “Boba balls” without affecting sensory properties.
Keywords: Boba; alginate beads; in vitro digestion; pomegranate peel extract; release kinetic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Rheological and antioxidant properties of chitosan/gelatin-based materials functionalized by pomegranate peel extract.Carbohydr Polym. 2020 Jan 15;228:115386. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115386. Epub 2019 Sep 28. Carbohydr Polym. 2020. PMID: 31635725
-
Chitosan Nanoparticles as a Promising Nanomaterial for Encapsulation of Pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) Peel Extract as a Natural Source of Antioxidants.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021 May 29;11(6):1439. doi: 10.3390/nano11061439. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34072520 Free PMC article.
-
Designing and fabrication of colloidal nano-phytosomes with gamma-oryzanol and phosphatidylcholine for encapsulation and delivery of polyphenol-rich extract from pomegranate peel.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Jan;256(Pt 2):128501. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.128501. Epub 2023 Nov 29. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 38040148
-
The bioactivity and applications of pomegranate peel extract: A review.J Food Biochem. 2022 Jul;46(7):e14105. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.14105. Epub 2022 Feb 6. J Food Biochem. 2022. PMID: 35128669 Review.
-
Pomegranate peel extract - A natural bioactive addition to novel active edible packaging.Food Res Int. 2022 Jun;156:111378. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111378. Epub 2022 May 14. Food Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35650986 Review.
Cited by
-
Encapsulation of Polyphenolic Preparation in Gelatin Fruit Jellies Slows the Digestive Release of Cholinesterase Inhibitors In Vitro.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Apr 29;14(5):535. doi: 10.3390/antiox14050535. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40427417 Free PMC article.
-
Agro-Food Waste as an Ingredient in Functional Beverage Processing: Sources, Functionality, Market and Regulation.Foods. 2023 Apr 8;12(8):1583. doi: 10.3390/foods12081583. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37107379 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Koay K.Y., Cheah C.W. Understanding consumers’ intention to revisit bubble tea stores: An application of the theory of planned behaviour. Br. Food J. 2022. ahead-of-print . - DOI
-
- Liu S., Xiao J., Feng Y., Zhang M., Li Y., Tu J., Niu L. Anthocyanin-fortified konjac glucomannan/sodium alginate composite edible boba: Characteristics of texture, microstructure, in vitro release behaviour and antioxidant capacity. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022;57:1791–1803. doi: 10.1111/ijfs.15557. - DOI
-
- Bennacef C., Desobry-Banon S., Probst L., Desobry S. Advances on alginate use for spherification to encapsulate biomolecules. Food Hydrocoll. 2021;118:106782. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.106782. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

