Factors Influencing Biofilm Formation by Salmonella enterica sv. Typhimurium, E. cloacae, E. hormaechei, Pantoea spp., and Bacillus spp. Isolated from Human Milk Determined by PCA Analysis
- PMID: 36496670
- PMCID: PMC9738827
- DOI: 10.3390/foods11233862
Factors Influencing Biofilm Formation by Salmonella enterica sv. Typhimurium, E. cloacae, E. hormaechei, Pantoea spp., and Bacillus spp. Isolated from Human Milk Determined by PCA Analysis
Abstract
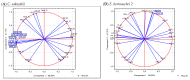
Bacteria enter milk during poor hygiene practices and can form a biofilm on surfaces that come into contact with human milk. The presence of a biofilm increases the risk of infections among newborns as bacteria protected by biofilm are resistant to washing and disinfection processes. The formation of the biofilm depends on the microbial species, environmental conditions, and the specific materials colonized. The aim of this study is to analyze the effects of factors such as temperature, incubation time, and initial cell concentration on biofilm formation by pathogenic bacteria isolated from human milk on model hydrophobic polystyrene surfaces. Model studies confirm that pathogenic bacteria appearing in human milk as a result of cross-contamination tend to form a biofilm. The majority of isolates formed biofilm at both 25 and 37 °C after 12 h at 1 × 103 CFU/mL inoculum count. Multivariate principal component analysis (PCA) showed that at lower temperatures, biofilm formation by bacterial isolates was the main determinant of biofilm formation, other factors were less important; however, at 37 °C, time was a factor in biofilm formation. The model research performed underlines the importance of maintaining the proper hygiene of rooms, surfaces, and devices for expressing, storing, and preparing mothers' milk and powdered infant formula (PIF) in facilities responsible for feeding newborns and premature babies.
Keywords: PCA; bacterial biofilm; breast milk; pathogen; polystyrene.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A systematic characterization of the distribution, biofilm-forming potential and the resistance of the biofilms to the CIP processes of the bacteria in a milk powder processing factory.Food Res Int. 2018 Nov;113:316-326. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2018.07.020. Epub 2018 Jul 19. Food Res Int. 2018. PMID: 30195526
-
Effect of Food Residues in Biofilm Formation on Stainless Steel and Polystyrene Surfaces by Salmonella enterica Strains Isolated from Poultry Houses.Foods. 2017 Nov 29;6(12):106. doi: 10.3390/foods6120106. Foods. 2017. PMID: 29186017 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetics of biofilm formation by pathogenic and spoilage microorganisms under conditions that mimic the poultry, meat, and egg processing industries.Int J Food Microbiol. 2019 Aug 16;303:32-41. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2019.04.012. Epub 2019 May 11. Int J Food Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31129476
-
Scanning electron microscopy of Salmonella biofilms on various food-contact surfaces in catfish mucus.Food Microbiol. 2018 Sep;74:143-150. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2018.03.013. Epub 2018 Mar 29. Food Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29706330
-
Neonatal enteral feeding tubes as loci for colonisation by members of the Enterobacteriaceae.BMC Infect Dis. 2009 Sep 1;9:146. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-9-146. BMC Infect Dis. 2009. PMID: 19723318 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Horizontal Gene Transfer of Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Biofilms.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Feb 4;12(2):328. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12020328. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36830238 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bowen A., Wiesenfeld H.C., Kloesz J.L., Pasculle A.W., Nowalk A.J., Brink L., Elliot E., Martin H., Tarr C.L. Notes from the field: Cronobacter sakazakii infection associated with feeding extrinsically contaminated expressed human milk to a premature infant—Pennsylvania, 2016. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2017;66:761–762. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6628a5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sundararajan M., Enane L.A., Kidwell L.A., Gentry R., Danao S., Bhumbra S., Lehmann C., Teachout M., Yeadon-Fagbohun J., Krombach P., et al. Notes from the field: Cronobacter sakazakii meningitis in a full-term neonate fed exclusively with breast milk—Indiana, 2018. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2018;67:12–48. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6744a7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

