Coordination of LMO7 with FAK Signaling Sustains Epithelial Integrity in Renal Epithelia Exposed to Osmotic Pressure
- PMID: 36497072
- PMCID: PMC9741450
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11233805
Coordination of LMO7 with FAK Signaling Sustains Epithelial Integrity in Renal Epithelia Exposed to Osmotic Pressure
Abstract
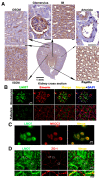
The kidney epithelial barrier has multifaceted functions in body fluids, electrolyte homeostasis, and urine production. The renal epithelial barrier (REB) frequently faces and challenges osmotic dynamics, which gives rise to osmotic pressure (a physical force). Osmotic pressure overloading can crack epithelial integrity and damage the REB. The endurance of REB to osmotic pressure forces remains obscure. LMO7 (LIM domain only 7) is a protein associated with the cell-cell junctional complex and cortical F-actin. Its upregulation was observed in cells cultured under hypertonic conditions. LMO7 is predominantly distributed in renal tubule epithelial cells. Hypertonic stimulation leads to LMO7 and F-actin assembly in the cortical stress fibers of renal epithelial cells. Hypertonic-isotonic alternation, as a pressure force pushing the plasma membrane inward/outward, was set as osmotic disturbance and was applied to test FAK signaling and LMO7 functioning in maintaining junctional integrity. LMO7 depletion in cells resulted in junctional integrity loss in the epithelial sheet-cultured hypertonic medium or hypertonic-isotonic alternation. Conversely, FAK inhibition by PF-573228 led to failure in robust cortical F-actin assembly and LMO7 association with cortical F-actin in epithelial cells responding to hypertonic stress. Epithelial integrity against osmotic stress and LMO7 and FAK signaling are involved in assembling robust cortical F-actin and maintaining junctional integrity. LMO7 elaborately manages FAK activation in renal epithelial cells, which was demonstrated excessive FAK activation present in LMO7 depleted NRK-52E cells and epithelial integrity loss when cells with LMO7 depletion were exposed to a hypertonic environment. Our data suggests that LMO7 regulates FAK activation and is responsible for maintaining REB under osmotic disturbance.
Keywords: FAK hypertonicity; LMO7; cortical stress fiber; epithelial barrier; epithelial integrity; osmotic stress; secretome.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no competing financial interest, such as consultancies, stock ownership or other equity interests or patent-licensing arrangements.
Figures






References
-
- Hara M., Minami Y., Ohashi M., Tsuchiya Y., Kusaba T., Tamagaki K., Koike N., Umemura Y., Inokawa H., Yagita K. Robust circadian clock oscillation and osmotic rhythms in inner medulla reflecting cortico-medullary osmotic gradient rhythm in rodent kidney. Sci. Rep. 2017;7:7306. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-07767-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Roffay C., Molinard G., Kim K., Urbanska M., Andrade V., Barbarasa V., Nowak P., Mercier V., Garcia-Calvo J., Matile S., et al. Passive coupling of membrane tension and cell volume during active response of cells to osmosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2021;118:e2103228118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2103228118. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

