Dying of Stress: Chemotherapy, Radiotherapy, and Small-Molecule Inhibitors in Immunogenic Cell Death and Immunogenic Modulation
- PMID: 36497086
- PMCID: PMC9737874
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11233826
Dying of Stress: Chemotherapy, Radiotherapy, and Small-Molecule Inhibitors in Immunogenic Cell Death and Immunogenic Modulation
Abstract
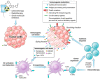
Innovative strategies to re-establish the immune-mediated destruction of malignant cells is paramount to the success of anti-cancer therapy. Accumulating evidence suggests that radiotherapy and select chemotherapeutic drugs and small molecule inhibitors induce immunogenic cell stress on tumors that results in improved immune recognition and targeting of the malignant cells. Through immunogenic cell death, which entails the release of antigens and danger signals, and immunogenic modulation, wherein the phenotype of stressed cells is altered to become more susceptible to immune attack, radiotherapies, chemotherapies, and small-molecule inhibitors exert immune-mediated anti-tumor responses. In this review, we discuss the mechanisms of immunogenic cell death and immunogenic modulation and their relevance in the anti-tumor activity of radiotherapies, chemotherapies, and small-molecule inhibitors. Our aim is to feature the immunological aspects of conventional and targeted cancer therapies and highlight how these therapies may be compatible with emerging immunotherapy approaches.
Keywords: chemotherapy; combination therapy; immunogenic cell death; immunogenic cell stress; immunogenic modulation; immunotherapy; radiotherapy; small molecule inhibitor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Stress-induced cellular responses in immunogenic cell death: Implications for cancer immunotherapy.Biochem Pharmacol. 2018 Jul;153:12-23. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2018.02.006. Epub 2018 Feb 10. Biochem Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29438676 Review.
-
From Immunogenic Cell Death to Immunogenic Modulation: Select Chemotherapy Regimens Induce a Spectrum of Immune-Enhancing Activities in the Tumor Microenvironment.Front Oncol. 2021 Aug 23;11:728018. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.728018. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34497771 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemotherapeutic drug-induced immunogenic cell death for nanomedicine-based cancer chemo-immunotherapy.Nanoscale. 2021 Oct 28;13(41):17218-17235. doi: 10.1039/d1nr05512g. Nanoscale. 2021. PMID: 34643196 Review.
-
Immunogenic chemotherapy: Dose and schedule dependence and combination with immunotherapy.Cancer Lett. 2018 Apr 10;419:210-221. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2018.01.050. Cancer Lett. 2018. PMID: 29414305 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Trial watch: chemotherapy-induced immunogenic cell death in oncology.Oncoimmunology. 2023 Jun 3;12(1):2219591. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2023.2219591. eCollection 2023. Oncoimmunology. 2023. PMID: 37284695 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Alum-anchored IL-12 combined with cytotoxic chemotherapy and immune checkpoint blockade enhanced antitumor immune responses in head and neck cancer models.J Immunother Cancer. 2024 Oct 23;12(10):e009712. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2024-009712. J Immunother Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39448201 Free PMC article.
-
Shifting cold to hot tumors by nanoparticle-loaded drugs and products.Clin Transl Oncol. 2025 Jan;27(1):42-69. doi: 10.1007/s12094-024-03577-3. Epub 2024 Jun 26. Clin Transl Oncol. 2025. PMID: 38922537 Review.
-
Clinical application of immunogenic cell death inducers in cancer immunotherapy: turning cold tumors hot.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 May 7;12:1363121. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1363121. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 38774648 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A landscape of checkpoint blockade resistance in cancer: underlying mechanisms and current strategies to overcome resistance.Cancer Biol Ther. 2024 Dec 31;25(1):2308097. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2024.2308097. Epub 2024 Feb 2. Cancer Biol Ther. 2024. PMID: 38306161 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systemic Immunological Changes After Yttrium-90 Radioembolization: A Pilot Prospective Observational Study-Clinical Insights.Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2024 Nov;47(11):1461-1470. doi: 10.1007/s00270-024-03870-2. Epub 2024 Oct 15. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2024. PMID: 39406871
References
-
- Galluzzi L., Vitale I., Warren S., Adjemian S., Agostinis P., Martinez A.B., Chan T.A., Coukos G., Demaria S., Deutsch E., et al. Consensus guidelines for the definition, detection and interpretation of immunogenic cell death. J. Immunother. Cancer. 2020;8:e000337. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2019-000337. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Galluzzi L., Vitale I., Aaronson S.A., Abrams J.M., Adam D., Agostinis P., Alnemri E.S., Altucci L., Amelio I., Andrews D.W., et al. Molecular mechanisms of cell death: Recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2018. Cell Death Differ. 2018;25:486–541. doi: 10.1038/s41418-017-0012-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

