Genome-Wide Association Study Identifies CDKN1A as a Novel Locus Associated with Muscle Fiber Composition
- PMID: 36497168
- PMCID: PMC9737696
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11233910
Genome-Wide Association Study Identifies CDKN1A as a Novel Locus Associated with Muscle Fiber Composition
Abstract
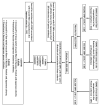
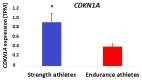
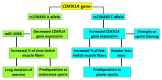
Muscle fiber composition is associated with physical performance, with endurance athletes having a high proportion of slow-twitch muscle fibers compared to power athletes. Approximately 45% of muscle fiber composition is heritable, however, single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) underlying inter-individual differences in muscle fiber types remain largely unknown. Based on three whole genome SNP datasets, we have shown that the rs236448 A allele located near the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A (CDKN1A) gene was associated with an increased proportion of slow-twitch muscle fibers in Russian (n = 151; p = 0.039), Finnish (n = 287; p = 0.03), and Japanese (n = 207; p = 0.008) cohorts (meta-analysis: p = 7.9 × 10−5. Furthermore, the frequency of the rs236448 A allele was significantly higher in Russian (p = 0.045) and Japanese (p = 0.038) elite endurance athletes compared to ethnically matched power athletes. On the contrary, the C allele was associated with a greater proportion of fast-twitch muscle fibers and a predisposition to power sports. CDKN1A participates in cell cycle regulation and is suppressed by the miR-208b, which has a prominent role in the activation of the slow myofiber gene program. Bioinformatic analysis revealed that the rs236448 C allele was associated with increased CDKN1A expression in whole blood (p = 8.5 × 10−15) and with greater appendicular lean mass (p = 1.2 × 10−5), whereas the A allele was associated with longer durations of exercise (p = 0.044) reported amongst the UK Biobank cohort. Furthermore, the expression of CDKN1A increased in response to strength (p < 0.0001) or sprint (p = 0.00035) training. Accordingly, we found that CDKN1A expression is significantly (p = 0.002) higher in the m. vastus lateralis of strength athletes compared to endurance athletes and is positively correlated with the percentage of fast-twitch muscle fibers (p = 0.018). In conclusion, our data suggest that the CDKN1A rs236448 SNP may be implicated in the determination of muscle fiber composition and may affect athletic performance.
Keywords: DNA; GWAS; athletic performance; endurance; exercise; genetic markers; genotype; muscle fibers; sports; sprinters; talent identification.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Klitgaard H., Mantoni M., Schiaffino S., Ausoni S., Gorza L., Laurent-Winter C., Schnohr P., Saltin B. Function, morphology and protein expression of ageing skeletal muscle, a cross-sectional study of elderly men with different training backgrounds. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1990;140:41–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1990.tb08974.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hall E.C.R., Lysenko E.A., Semenova E.A., Borisov O.V., Andryushchenko O.N., Andryushchenko L.B., Vepkhvadze T.F., Lednev E.M., Zmijewski P., Popov D.V., et al. Prediction of muscle fiber composition using multiple repetition testing. Biol. Sport. 2021;38:277–283. doi: 10.5114/biolsport.2021.99705. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R00 DK099240/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K99 DK099240/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MC_QA137853/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 DK072193/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 HG000196/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- ZIA HG000024/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- MC_PC_17228/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- F32 HG000196/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG003079/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

