The microRNA Lifecycle in Health and Cancer
- PMID: 36497229
- PMCID: PMC9736740
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14235748
The microRNA Lifecycle in Health and Cancer
Abstract
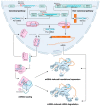
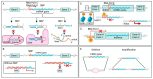
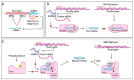
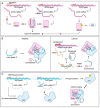
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-coding RNAs of ~22 nucleotides that regulate gene expression at the post-transcriptional level. They can bind to around 60% of all protein-coding genes with an average of 200 targets per miRNA, indicating their important function within physiological and pathological cellular processes. miRNAs can be quickly produced in high amounts through canonical and non-canonical pathways that involve a multitude of steps and proteins. In cancer, miRNA biogenesis, availability and regulation of target expression can be altered to promote tumour progression. This can be due to genetic causes, such as single nucleotide polymorphisms, epigenetic changes, differences in host gene expression, or chromosomal remodelling. Alternatively, post-transcriptional changes in miRNA stability, and defective or absent components and mediators of the miRNA-induced silencing complex can lead to altered miRNA function. This review provides an overview of the current knowledge on the lifecycle of miRNAs in health and cancer. Understanding miRNA function and regulation is fundamental prior to potential future application of miRNAs as cancer biomarkers.
Keywords: biogenesis; biomarkers; cancer; genetic alterations; microRNA; post-translational regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Exploring Mechanisms of MicroRNA Downregulation in Cancer.Microrna. 2017;6(1):2-16. doi: 10.2174/2211536605666161208154633. Microrna. 2017. PMID: 27928946 Review.
-
Regulation of microRNA biogenesis.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014 Aug;15(8):509-24. doi: 10.1038/nrm3838. Epub 2014 Jul 16. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 25027649 Review.
-
Plant microRNAs: biogenesis, gene silencing, web-based analysis tools and their use as molecular markers.3 Biotech. 2019 Nov;9(11):413. doi: 10.1007/s13205-019-1942-y. Epub 2019 Oct 23. 3 Biotech. 2019. PMID: 31696018 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overview of MicroRNA Biogenesis, Mechanisms of Actions, and Circulation.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018 Aug 3;9:402. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00402. eCollection 2018. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018. PMID: 30123182 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dissecting miRNA facilitated physiology and function in human breast cancer for therapeutic intervention.Semin Cancer Biol. 2021 Jul;72:46-64. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2020.05.017. Epub 2020 Jun 1. Semin Cancer Biol. 2021. PMID: 32497683 Review.
Cited by
-
Insights into Online microRNA Bioinformatics Tools.Noncoding RNA. 2023 Mar 6;9(2):18. doi: 10.3390/ncrna9020018. Noncoding RNA. 2023. PMID: 36960963 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity.Biomolecules. 2023 Mar 20;13(3):568. doi: 10.3390/biom13030568. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 36979503 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Strategy for Pre-Clinical Development of Active Targeting MicroRNA Oligonucleotide Therapeutics for Unmet Medical Needs.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 12;24(8):7126. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087126. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108289 Free PMC article.
-
Immune checkpoints and ncRNAs: pioneering immunotherapy approaches for hematological malignancies.Cancer Cell Int. 2024 Dec 19;24(1):410. doi: 10.1186/s12935-024-03596-8. Cancer Cell Int. 2024. PMID: 39702293 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating miRNA's biomarkers for early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma in Egyptian patients based on machine learning algorithms.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 29;14(1):4989. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-54795-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38424116 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

