Insights on the Role of PGRMC1 in Mitotic and Meiotic Cell Division
- PMID: 36497237
- PMCID: PMC9736406
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14235755
Insights on the Role of PGRMC1 in Mitotic and Meiotic Cell Division
Abstract
During mitosis, chromosome missegregation and cytokinesis defects have been recognized as hallmarks of cancer cells. Cytoskeletal elements composing the spindle and the contractile ring and their associated proteins play crucial roles in the faithful progression of mitotic cell division. The hypothesis that PGRMC1, most likely as a part of a yet-to-be-defined complex, is involved in the regulation of spindle function and, more broadly, the cytoskeletal machinery driving cell division is particularly appealing. Nevertheless, more than ten years after the preliminary observation that PGRMC1 changes its localization dynamically during meiotic and mitotic cell division, this field of research has remained a niche and needs to be fully explored. To encourage research in this fascinating field, in this review, we will recap the current knowledge on PGRMC1 function during mitotic and meiotic cell division, critically highlighting the strengths and limitations of the experimental approaches used so far. We will focus on known interacting partners as well as new putative associated proteins that have recently arisen in the literature and that might support current as well as new hypotheses of a role for PGRMC1 in specific spindle subcompartments, such as the centrosome, kinetochores, and the midzone/midbody.
Keywords: cell division; cytokinesis; cytoskeleton; meiosis; mitosis; progesterone receptor membrane component 1; spindle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
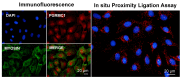
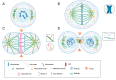
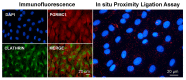
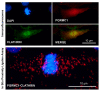
Similar articles
-
PGRMC1 participates in late events of bovine granulosa cells mitosis and oocyte meiosis.Cell Cycle. 2016 Aug 2;15(15):2019-32. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2016.1192731. Epub 2016 Jun 3. Cell Cycle. 2016. PMID: 27260975 Free PMC article.
-
The active form of the metabolic sensor: AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) directly binds the mitotic apparatus and travels from centrosomes to the spindle midzone during mitosis and cytokinesis.Cell Cycle. 2009 Aug;8(15):2385-98. doi: 10.4161/cc.8.15.9082. Epub 2009 Aug 21. Cell Cycle. 2009. PMID: 19556893
-
Polo-like kinase 1 regulates activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) at the mitotic apparatus.Cell Cycle. 2011 Apr 15;10(8):1295-302. doi: 10.4161/cc.10.8.15342. Epub 2011 Apr 15. Cell Cycle. 2011. PMID: 21474997
-
Review: The putative role of Progesterone Receptor membrane Component 1 in bovine oocyte development and competence.Animal. 2023 May;17 Suppl 1:100783. doi: 10.1016/j.animal.2023.100783. Animal. 2023. PMID: 37567656 Review.
-
Rho GTPases as regulators of mitosis and cytokinesis in mammalian cells.Small GTPases. 2014;5:e29770. doi: 10.4161/sgtp.29770. Epub 2014 Jul 2. Small GTPases. 2014. PMID: 24988197 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Uterine Pgrmc2 Deficiency Attenuates Endometrial Hyperplasia and Cancer and Prolongs Lifespan in a Pten Loss-of-Function-Induced Cancer Model.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Mar 31;17(7):1178. doi: 10.3390/cancers17071178. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40227710 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro chemo-preventive efficacy of synthetic progestin Norethindrone in human epithelial ovarian cancer.Med Oncol. 2023 Jun 3;40(7):195. doi: 10.1007/s12032-023-02061-2. Med Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37270458
-
PGRMC1 and PAQR4 are promising molecular targets for a rare subtype of ovarian cancer.Open Life Sci. 2024 Oct 26;19(1):20220982. doi: 10.1515/biol-2022-0982. eCollection 2024. Open Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39464509 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

