Staging Breast Cancer with MRI, the T. A Key Role in the Neoadjuvant Setting
- PMID: 36497265
- PMCID: PMC9739275
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14235786
Staging Breast Cancer with MRI, the T. A Key Role in the Neoadjuvant Setting
Abstract
Breast cancer (BC) is the most common cancer among women worldwide. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT) indications have expanded from inoperable locally advanced to early-stage breast cancer. Achieving a pathological complete response (pCR) has been proven to be an excellent prognostic marker leading to better disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS). Although diagnostic accuracy of MRI has been shown repeatedly to be superior to conventional methods in assessing the extent of breast disease there are still controversies regarding the indication of MRI in this setting. We intended to review the complex literature concerning the tumor size in staging, response and surgical planning in patients with early breast cancer receiving NACT, in order to clarify the role of MRI. Morphological and functional MRI techniques are making headway in the assessment of the tumor size in the staging, residual tumor assessment and prediction of response. Radiomics and radiogenomics MRI applications in the setting of the prediction of response to NACT in breast cancer are continuously increasing. Tailored therapy strategies allow considerations of treatment de-escalation in excellent responders and avoiding or at least postponing breast surgery in selected patients.
Keywords: early-stage breast cancer; magnetic resonance imaging; neoadjuvant chemotherapy; pathological complete response.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
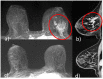
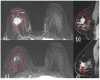
Similar articles
-
Accuracy of digital mammography, ultrasound and MRI in predicting the pathological complete response and residual tumor size of breast cancer after completion of neoadjuvant chemotherapy.Indian J Cancer. 2022 Jul-Sep;59(3):345-353. doi: 10.4103/ijc.IJC_795_19. Indian J Cancer. 2022. PMID: 33753611
-
Radiologic complete response (rCR) in contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (CE-MRI) after neoadjuvant chemotherapy for early breast cancer predicts recurrence-free survival but not pathologic complete response (pCR).Breast Cancer Res. 2019 Jan 31;21(1):19. doi: 10.1186/s13058-018-1091-y. Breast Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30704493 Free PMC article.
-
Accuracy of MRI Versus PET/CT in the Prediction of Treatment Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer.Cureus. 2024 Aug 4;16(8):e66114. doi: 10.7759/cureus.66114. eCollection 2024 Aug. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39108769 Free PMC article.
-
Overview of resistance to systemic therapy in patients with breast cancer.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;608:1-22. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-74039-3_1. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007. PMID: 17993229 Review.
-
Surgical Planning after Neoadjuvant Treatment in Breast Cancer: A Multimodality Imaging-Based Approach Focused on MRI.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Feb 24;15(5):1439. doi: 10.3390/cancers15051439. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36900231 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnostics and Therapeutics in Early Stage Breast Cancer Receiving Neoadjuvant Systemic Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Oct 7;15(19):4874. doi: 10.3390/cancers15194874. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37835568 Free PMC article.
-
An Innovative Scoring System to Select the Optimal Surgery in Breast Cancer after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy.J Pers Med. 2023 Aug 21;13(8):1280. doi: 10.3390/jpm13081280. J Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 37623530 Free PMC article.
-
Abbreviated breast MRI for evaluating breast cancer before initiation of neoadjuvant chemotherapy: A cross-sectional study.Eur J Radiol Open. 2023 Aug 14;11:100517. doi: 10.1016/j.ejro.2023.100517. eCollection 2023 Dec. Eur J Radiol Open. 2023. PMID: 37609046 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial Intelligence-Enhanced Breast MRI: Applications in Breast Cancer Primary Treatment Response Assessment and Prediction.Invest Radiol. 2024 Mar 1;59(3):230-242. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000001010. Invest Radiol. 2024. PMID: 37493391 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Head‑to‑head comparison of contrast‑enhanced mammography and MRI in assessing the tumor response to neoadjuvant therapy in breast cancer: a prospective, multireader study.Radiol Med. 2025 Aug 12. doi: 10.1007/s11547-025-02068-x. Online ahead of print. Radiol Med. 2025. PMID: 40794243
References
-
- Curigliano G., Burstein H.J., Winer E.P., Gnant M., Dubsky P., Loibl S., Colleoni M., Regan M.M., Piccart-Gebhart M., Senn H.J., et al. De- escalating and escalating treatments for early-stage breast cancer: The St. Gallen international expert consensus conference on the primary therapy of early breast cancer 2017. Ann. Oncol. 2018;29:2153. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdx806. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

