C-Reactive Protein Pretreatment-Level Evaluation for Ewing's Sarcoma Prognosis Assessment-A 15-Year Retrospective Single-Centre Study
- PMID: 36497377
- PMCID: PMC9735882
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14235898
C-Reactive Protein Pretreatment-Level Evaluation for Ewing's Sarcoma Prognosis Assessment-A 15-Year Retrospective Single-Centre Study
Abstract
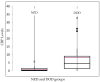
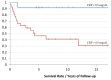
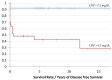
Background: A pathological/inflamed cellular microenvironment state is an additional risk factor for any cancer type. The importance of a chronic inflammation state in most diffuse types of tumour has already been analysed, except for in Ewing’s sarcoma. It is a highly malignant blue round cell tumour, with 90% of cases occurring in patients aged between 5 and 25 years. Worldwide, 2.9 out of 1,000,000 children per year are affected by this malignancy. The aim of this retrospective study was to analyse the role of C-reactive protein (CRP) as a prognostic factor for Ewing’s sarcomas. Methods: This retrospective study at Klinikum rechts der Isar included 82 patients with a confirmed Ewing’s sarcoma diagnosis treated between 2004 and 2019. Preoperative CRP determination was assessed in mg/dL with a normal value established as below 0.5 mg/dL. Disease-free survival time was calculated as the time between the initial diagnosis and an event such as local recurrence or metastasis. Follow-up status was described as death of disease (DOD), no evidence of disease (NED) or alive with disease (AWD). The exclusion criteria of this study included insufficient laboratory values and a lack of information regarding the follow-up status or non-oncological resection. Results: Serum CRP levels were significantly different in patients with a poorer prognosis (DOD) and in patients who presented distant metastasis (p = 0.0016 and p = 0.009, respectively), whereas CRP levels were not significantly different in patients with local recurrence (p = 0.02). The optimal breakpoint that predicted prognosis was 0.5 mg/dL, with a sensitivity of 0.76 and a specificity of 0.74 (AUC 0.81). Univariate CRP analysis level >0.5 mg/dL revealed a hazard ratio of 9.5 (95% CI 3.5−25.5). Conclusions: In Ewing’s sarcoma cases, we consider a CRP pretreatment value >0.5 mg/dL as a sensitive prognostic risk factor indication for distant metastasis and poor prognosis. Further research with more data is required to determine more sensitive cutoff levels.
Keywords: CRP; Ewing’s sarcoma; local recurrence; metastasis; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Prognostic Value of the Serum Level of C-Reactive Protein for Survival of Children with Ewing's Sarcoma.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Mar 3;15(5):1573. doi: 10.3390/cancers15051573. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36900365 Free PMC article.
-
Which Factors Are Associated with Local Control and Survival of Patients with Localized Pelvic Ewing's Sarcoma? A Retrospective Analysis of Data from the Euro-EWING99 Trial.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2020 Feb;478(2):290-302. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000000962. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2020. PMID: 31580267 Free PMC article.
-
[Ewing's sarcoma in children--current surgical treatment options, evaluation of our patients].Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2004;71(4):220-7. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2004. PMID: 15456100 Czech.
-
Multimodality treatment of intradural extramedullary Ewing's sarcomas. A systematic review.Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2018 Jan;164:169-181. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2017.11.014. Epub 2017 Dec 7. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2018. PMID: 29247908
-
Infantile intraorbital Ewing's sarcoma: case report and review of the literature.Childs Nerv Syst. 2021 Jan;37(1):299-304. doi: 10.1007/s00381-020-04606-6. Epub 2020 Apr 20. Childs Nerv Syst. 2021. PMID: 32314023 Review.
Cited by
-
The Prognostic Value of the Serum Level of C-Reactive Protein for Survival of Children with Ewing's Sarcoma.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Mar 3;15(5):1573. doi: 10.3390/cancers15051573. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36900365 Free PMC article.
-
TCR-transgenic T cells and YB-1-based oncolytic virotherapy improve survival in a preclinical Ewing sarcoma xenograft mouse model.Front Immunol. 2024 Jan 22;15:1330868. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1330868. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38318175 Free PMC article.
-
C-Reactive Protein Pretreatment-Level Evaluation with Histopathological Correlation for Chondrosarcoma Prognosis Assessment-A 15-Year Retrospective Single-Center Study.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Jul 4;14(13):1428. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14131428. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39001318 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Picci P., Manfrini M., Fabbri N., Gambarotti M., Vanel D. Atlas of Musculoskeletal Tumors and Tumorlike Lesions: The Rizzoli Case Archive. Springer International Publishing; Cham, Switzerland: 2016.
-
- Ahmed S.K., Witten B.G., Harmsen W.S., Rose P.S., Krailo M., Marcus K.J., Randall R.L., DuBois S.G., Janeway K.A., Womer R.B., et al. Analysis of local control outcomes and clinical prognostic factors in localized pelvic Ewing sarcoma patients treated with radiation therapy: A Report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2022 doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2022.07.1840. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Indelicato D.J., Vega R.B.M., Viviers E., Morris C.G., Bradfield S.M., Ranalli N.J., Bradley J.A. Modern Therapy for Spinal and Paraspinal Ewing Sarcoma: An Update of the University of Florida Experience. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2022;113:161–165. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2022.01.007. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Durer S., Shaikh H. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2022. Ewing Sarcoma. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

