The Impact of Facility Surgical Caseload Volumes on Survival Outcomes in Patients Undergoing Radical Cystectomy
- PMID: 36497466
- PMCID: PMC9735798
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14235984
The Impact of Facility Surgical Caseload Volumes on Survival Outcomes in Patients Undergoing Radical Cystectomy
Abstract
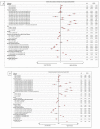
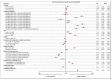
The role of surgical experience and its impact on the survival requires further investigation. A cohort of patients undergoing radical cystectomy or anterior pelvic exenteration for localized bladder cancer between 2006 and 2013 at 1143 facilities across the United States was identified using the National Cancer Database and analyzed. Using overall survival (OS) as the primary outcome, the relationship between facility annual caseload (FAC) and facility annual surgical caseload (FASC) for those undergoing curative surgery was examined. Four volume groups (VG) depending on caseload using both FAC and FASC were defined. These included VG1: below 50th percentile, VG2: 50th−74th percentile, VG3: 75th−89th percentile, and VG4: 90th and above. Between 2006 and 2013, 27,272 patients underwent surgery for localized bladder cancer. The median OS was 59.66 months (95% CI: 57.79−61.77). OS improved significantly as caseload increased. The unadjusted median OS difference between VG1 and VG4 was 15.35 months (64.3 vs. 48.95 months, HR 1.19 95% CI: 1.13−1.25, p < 0.001) for FAC. This figure was 19.84 months (66.89 vs. 47.05 months, HR 1.25 95% CI: 1.18−1.32, p < 0.0001) for FASC. This analysis revealed a significant and clinically important survival advantage for curative bladder cancer surgery at highly experienced centers.
Keywords: NCDB; bladder cancer; facility caseload; national cancer database; oncologic outcomes; overall survival; pelvic exenteration; radical cystectomy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Influence of the facility caseload on the subsequent survival of men with localized prostate cancer undergoing radical prostatectomy.Cancer. 2019 Nov 1;125(21):3853-3863. doi: 10.1002/cncr.32290. Epub 2019 Aug 9. Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31398279 Free PMC article.
-
Hospital and surgical caseload are predictors of comprehensive surgical treatment for bladder cancer: a population based study.J Urol. 2011 Sep;186(3):824-8. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2011.04.066. Epub 2011 Jul 23. J Urol. 2011. PMID: 21788051
-
Comparative effectiveness of robot-assisted vs. open radical cystectomy.Urol Oncol. 2018 Mar;36(3):88.e1-88.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2017.09.018. Epub 2017 Dec 23. Urol Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29277584
-
Complications of radical cystectomy.Minerva Urol Nefrol. 2007 Mar;59(1):67-87. Minerva Urol Nefrol. 2007. PMID: 17431372 Review.
-
Association between Smoking Exposure, Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Response and Survival Outcomes following Radical Cystectomy: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Urol. 2020 Oct;204(4):649-660. doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000000813. Epub 2020 Feb 27. J Urol. 2020. PMID: 32105187
Cited by
-
Preoperative Physical Activity Improvement with the Use of Activity Trackers in Patients Undergoing Radical Cystectomy-A Bicentric, Open-label, Randomised Controlled Trial: A Clinical Study Protocol of the PreAct Trial.Eur Urol Open Sci. 2024 Dec 10;71:78-86. doi: 10.1016/j.euros.2024.11.003. eCollection 2025 Jan. Eur Urol Open Sci. 2024. PMID: 39758853 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of hospital caseload on perioperative mortality, morbidity and costs in bladder cancer patients undergoing radical cystectomy: results of the German nationwide inpatient data.World J Urol. 2024 Jan 10;42(1):19. doi: 10.1007/s00345-023-04742-z. World J Urol. 2024. PMID: 38197902 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nuttall M., Van Der Meulen J., Phillips N., Sharpin C., Gillatt D., McIntosh G., Emberton M. A systematic review and critique of the literature relating hospital or surgeon volume to health outcomes for 3 urological cancer procedures. (6 Pt 1)J. Urol. 2004;172:2145–2152. doi: 10.1097/01.ju.0000140257.05714.45. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

