The Spatial-Temporal Transition and Influencing Factors of Green and Low-Carbon Utilization Efficiency of Urban Land in China under the Goal of Carbon Neutralization
- PMID: 36498222
- PMCID: PMC9739493
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph192316149
The Spatial-Temporal Transition and Influencing Factors of Green and Low-Carbon Utilization Efficiency of Urban Land in China under the Goal of Carbon Neutralization
Abstract
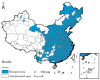
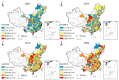
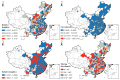
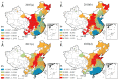
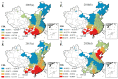
Urban-land development and utilization is one of the main sources of carbon emissions. Improving the green and low-carbon utilization efficiency of urban land (GLUEUL) under the goal of carbon neutrality is crucial to the low-carbon transition and green development of China's economy. Combining the concept of green and low-carbon development in urban land use, carbon emissions and industrial-pollution emissions are incorporated into the unexpected outputs of the GLUEUL evaluation system. The super-efficient slacks-based measure (SBM) model, Exploratory Spatial-Temporal Data Analysis (ESTDA) method and Geographically and Temporally Weighted Regression (GTWR) model were used to analyze the spatial-temporal transition and the influencing factors of GLUEUL in 282 cities in China from 2005 to 2020. The result shows that: (1) From 2005 to 2020, the green and low-carbon land-utilization efficiency of Chinese cities shows an increasing temporal-evolution trend, but the gap between cities is gradually widening. (2) From the spatial-temporal dynamic characteristics of Local Indicators of Spatial Association (LISA), regions with the highest GLUEUL have strong dynamics and instability, while cities at the lowest level have a relatively stable spatial structure. On the whole, the local-spatial-transfer direction of GLUEUL of each city is stable, with certain path-dependent characteristics. (3) There are differences in the degree of influence and direction of action of different factors on GLUEUL. The economic development level, industrial-structure upgrading, financial support, wealth level, and green-technology-innovation ability have positive effects on overall GLUEUL, with industrial-structure upgrading promoting GLUEUL the most, while urban population size, foreign-investment scale, and financial-development level play a negative role. This study can provide some empirical and theoretical references for the improvement of GLUEUL.
Keywords: GLUEUL; carbon neutrality; influencing factors; spatial-temporal transition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Tan S.K., Hu B.X., Kuang B., Zhou M. Regional differences and dynamic evolution of urban land green use efficiency within the Yangtze River Delta, China. Land Use Policy. 2021;106:105449. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2021.105449. - DOI
-
- Chen H., Meng C.Y., Cao Q. Measurement and Influencing Factors of Low Carbon Urban Land Use Efficiency-Based on Non-Radial Directional Distance Function. Land. 2022;11:1052. doi: 10.3390/land11071052. - DOI
-
- Griffin P.W., Hammond G.P., Norman J.B. Industrial energy use and carbon emissions reduction: A UK perspective. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Energy Environ. 2016;5:684–714. doi: 10.1002/wene.212. - DOI
-
- Cen X., Wu C., Xing X., Fang M., Grarang Z.M., Wu Y. Coupling intensive land use and landscape ecological security for urban sustainability: An integrated socioeconomic data and spatial metrics analysis in Hangzhou city. Sustainability. 2015;7:1459–1482. doi: 10.3390/su7021459. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

