Changes in the Enteric Neurons Containing Selected Active Substances in the Porcine Descending Colon after the Administration of Bisphenol A (BPA)
- PMID: 36498260
- PMCID: PMC9739061
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph192316187
Changes in the Enteric Neurons Containing Selected Active Substances in the Porcine Descending Colon after the Administration of Bisphenol A (BPA)
Abstract
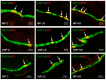
Bisphenol A (BPA) is an endocrine disruptor widely distributed in the environment due to its common use in the plastics industry. It is known that it has a strong negative effect on human and animal organisms, but a lot of aspects of this impact are still unexplored. This includes the impact of BPA on the enteric nervous system (ENS) in the large intestine. Therefore, the aim of the study was to investigate the influence of various doses of BPA on the neurons located in the descending colon of the domestic pig, which due to similarities in the organization of intestinal innervation to the human gastrointestinal tract is a good animal model to study processes occurring in human ENS. During this study, the double immunofluorescence technique was used. The obtained results have shown that BPA clearly affects the neurochemical characterization of the enteric neurons located in the descending colon. The administration of BPA caused an increase in the number of enteric neurons containing substance P (SP) and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) with a simultaneously decrease in the number of neurons positive for galanin (GAL) and vesicular acetylcholine transporter (VAChT used as a marker of cholinergic neurons). Changes were noted in all types of the enteric plexuses, i.e., the myenteric plexus, outer submucous plexus and inner submucous plexus. The intensity of changes depended on the dose of BPA and the type of enteric plexus studied. The results have shown that BPA may affect the descending colon through the changes in neurochemical characterization of the enteric neurons located in this segment of the gastrointestinal tract.
Keywords: bisphenol A; descending colon; enteric nervous system; porcine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

