The Impact of COVID-19 on the Sustainable Development Goals: Achievements and Expectations
- PMID: 36498340
- PMCID: PMC9739062
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph192316266
The Impact of COVID-19 on the Sustainable Development Goals: Achievements and Expectations
Abstract
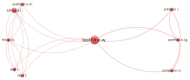
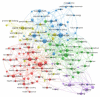
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on almost all the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), leaving no country unaffected. It has caused a shift in political agendas, but also in lines of research. At the same time, the world is trying to make the transition to a more sustainable economic model. The research objectives of this paper are to explore the impact of COVID-19 on the fulfilment of the SDGs with regard to the research of the scientific community, and to analyze the presence of the Circular Economy (CE) in the literature. To this end, this research applies bibliometric analysis and a systematic review of the literature, using VOSviewer for data visualization. Five clusters were detected and grouped according to the three dimensions of sustainability. The extent of the effects of the health, economic and social crisis resulting from the pandemic, in addition to the climate crisis, is still uncertain, but it seems clear that the main issues are inefficient waste management, supply chain issues, adaptation to online education and energy concerns. The CE has been part of the solution to this crisis, and it is seen as an ideal model to be promoted based on the opportunities detected.
Keywords: COVID-19; SDG; bibliometric analysis; circular economy; systematic review.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Nguyen T.L., Nguyen T.B.H., Nguyen T.H., Le V.L.H. Environmental protection policies at craft villages in Hanoi in the context of sustainable development. EDP Sci. 2021;258:05014. doi: 10.1051/e3sconf/202125805014. - DOI
-
- WCED World Commission on Environment and Development: Our Common Future. Oxford University Press; New York, NY, USA: 1987.
-
- United Nations “Agenda 21” A Sustainable Development Agenda for the 21st Century [Internet]; Proceedings of the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development; Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. 3–14 June 1992; [(accessed on 14 March 2022)]. Available online: https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/outcomedocuments/agenda21.
-
- United Nations . The Millennium Development Goals Report. United Nations; New York, NY, USA: 2000.
-
- United Nations . Transforming our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. United Nations; New York, NY, USA: 2015. Outcome Document for the UN Summit to Adopt the Post-2015 Development Agenda: Draft for Adoption.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

